mirror of
https://github.com/kubesphere/website.git
synced 2025-12-26 00:12:48 +00:00
commit
3cf6b3714d
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,596 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: '在 Kubernetes 中基于 StatefulSet 部署 MySQL(上)'
|
||||
tag: 'KubeSphere, Kubernetes, MySQL'
|
||||
keywords: 'KubeSphere, Kubernetes, MySQL, StatefulSet'
|
||||
description: '本文实现了 MySQL 数据库在基于 KubeSphere 部署的 K8s 集群上的安装部署,部署方式采用了图形化这种形式。'
|
||||
createTime: '2022-06-02'
|
||||
author: '张延英'
|
||||
snapshot: 'https://pek3b.qingstor.com/kubesphere-community/images/kubesphere-kubernetes-mysql-statefulset-cover.png'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**大家好,我是老 Z!**
|
||||
|
||||
本文实现了 MySQL 数据库在基于 KubeSphere 部署的 K8s 集群上的安装部署,部署方式采用了图形化这种形式。下一篇文章将会涉及 GitOps 的基础操作,部署过程涉及的所有 YAML 文件都会使用 Git 进行版本管理,并存放在 Git 仓库中,敬请期待!
|
||||
|
||||
本文部署的 MySQL 选择了比较保守的 5.7 系列,其他版本可能会有不同。本文的操作仅适用于小规模数据量且对可靠性和性能要求不高的数据库使用场景,例如开发测试环境、例如我生产环境的 Nacos 服务。生产环境或是重要的数据库个人不建议将数据放到 K8s 上,优先采用云服务商提供的 RDS,其次自己利用虚拟机搭建 MySQL 主从或是 Galera Cluster,且一定做好备份方案。
|
||||
|
||||
**数据库的可靠性、可用性是运维的重中之重,不容忽视,切记!!!**
|
||||
|
||||
### 本文知识点
|
||||
|
||||
- 定级:**入门级**
|
||||
- 单节点 MySQL 在 K8s 上的安装配置
|
||||
- KubeSphere 图形化部署工作负载
|
||||
- GitOps 入门
|
||||
- Git 常用操作
|
||||
- 配置代码如何实现在 GitHub 和 Gitee 保持同步
|
||||
- MySQL 性能测试基础
|
||||
- 运维思想、思路
|
||||
|
||||
### 演示服务器配置
|
||||
|
||||
| 主机名 | 操作系统 | IP | CPU | 内存 | 系统盘 | 数据盘 | 用途 |
|
||||
| :--------------: | :----------: | :--: | :--: | :----: | :----: | :------------------------------: | :------------------------------: |
|
||||
| zdeops-master | CentOS-7.9-x86_64 | 192.168.9.9 | 2 | 4 | 40 | 200 | Ansible 运维控制节点 |
|
||||
| ks-k8s-master-0 | CentOS-7.9-x86_64 | 192.168.9.91 | 8 | 32 | 40 | 200 | KubeSphere/k8s-master/k8s-worker |
|
||||
| ks-k8s-master-1 | CentOS-7.9-x86_64 | 192.168.9.92 | 8 | 32 | 40 | 200 | KubeSphere/k8s-master/k8s-worker |
|
||||
| ks-k8s-master-2 | CentOS-7.9-x86_64 | 192.168.9.93 | 8 | 32 | 40 | 200 | KubeSphere/k8s-master/k8s-worker |
|
||||
| glusterfs-node-0 | CentOS-7.9-x86_64 | 192.168.9.95 | 4 | 8 | 40 | 200 | GlusterFS/Elasticsearch |
|
||||
| glusterfs-node-1 | | 192.168.9.96 | 4 | 8 | 40 | 200 | GlusterFS/Elasticsearch |
|
||||
| glusterfs-node-2 | CentOS-7.9-x86_64 | 192.168.9.97 | 4 | 8 | 40 | 200 | GlusterFS/Elasticsearch |
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## MySQL 安装之旅
|
||||
|
||||
### 寻找参考文档
|
||||
|
||||
#### 我个人查找参考文档习惯的的寻找路径
|
||||
|
||||
- **官方网站**-精准定位
|
||||
- 官网有时没有相关文档、或是文档不够详细
|
||||
- 英文文档、阅读困难
|
||||
- **搜索关键字**-大海捞针
|
||||
- CSDN
|
||||
- 博客园
|
||||
- 某个人博客
|
||||
- 问答网站
|
||||
- 其他
|
||||
|
||||
#### 打开 [MySQL 官方网站](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/ "MySQL 官方网站")
|
||||
|
||||
选择 **MySQL5.7** 版本的 Reference Manual。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在 **Installing MySQL on Linux** 章节中,搜寻一番,发现在 [Deploying MySQL on Linux with Docker](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/linux-installation-docker.html "Deploying MySQL on Linux with Docker") 小节下两篇具有参考价值的文档,先去看看。
|
||||
|
||||
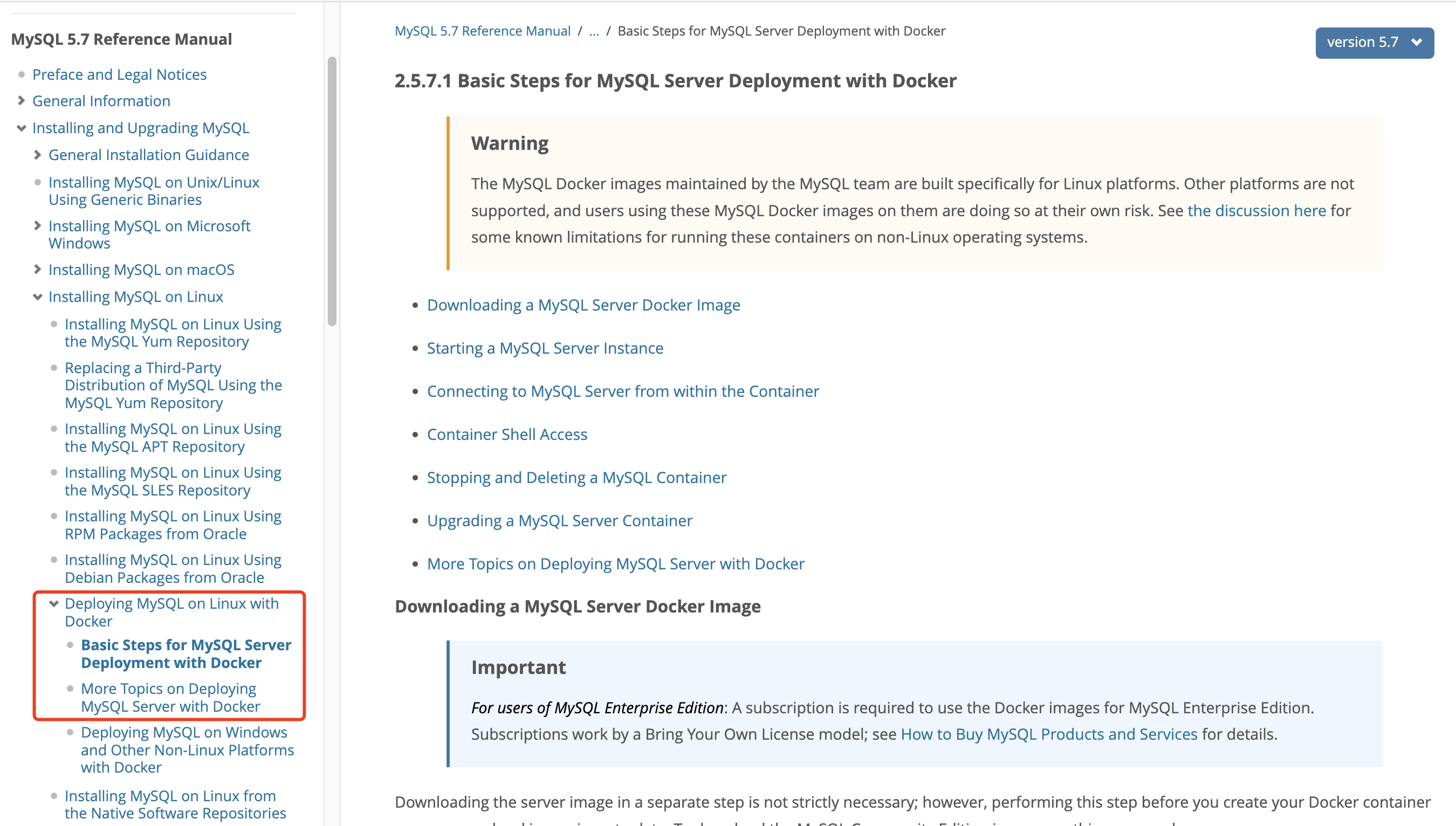
|
||||
|
||||
浏览完以后你会发现,只是学会了利用 Docker Image 安装 MySQL 的基本方法,细节不上图了。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然官方没有提到如何在 K8s 上部署 MySQL,但是我已经有 Docker 和 K8s 的基础知识了,先不去进行搜索吃别人的了,自己尝试在 K8s 上部署一个单节点的 MySQL。
|
||||
|
||||
### 尝试部署单节点 MySQL
|
||||
|
||||
#### 先梳理一下思路,部署一个 MySQL 我们需要准备哪些资源
|
||||
|
||||
- 在 Docker Hub 获取 MySQL 镜像。
|
||||
- 查看 MySQL 镜像说明,确定安装初始化参数。
|
||||
- MySQL 属于有状态服务,所以我们需要定义 StatefulSet 类型的资源。
|
||||
- 编写 StatefulSet 类型的 MySQL 资源定义文件-YAML。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 查看官方镜像说明,确定初始化参数
|
||||
|
||||
**如果之前有 Docker 部署 MySQL 的经验,这一步就很简单了,直接把参数配置搬过来就行。**
|
||||
|
||||
打开 https://hub.docker.com,搜索 mysql。
|
||||
|
||||
搜索结果中会有很多的 mysql,我重点关注了两个镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
- Docker 官方维护的 [mysql 仓库](https://hub.docker.com/_/mysql "mysql 仓库")
|
||||
- Oracle 的 MySQL 团队维护的 [mysql 仓库](https://hub.docker.com/r/mysql/mysql-server "mysql 仓库")
|
||||
|
||||
本次实验我使用了 Docker 官方维护的仓库,进入 MySQL 仓库页面。
|
||||
|
||||
大概浏览一遍,确认了几个必须要配置的地方(确定过程需要经验和技术积累)。
|
||||
|
||||
- 镜像:**mysql:5.7.38**
|
||||
- root 密码:**MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD**
|
||||
- 数据持久化存储目录:/var/lib/mysql
|
||||
|
||||
#### 利用 KubeSphere 部署 MySQL(V1 版)
|
||||
|
||||
确定了初始化的参数,接下来就开始部署 MySQL。
|
||||
|
||||
**按 K8s 常规套路编写资源定义 YAML 文件?NO!我现在是小白,手写配置文件太高端了,还不适合我。**
|
||||
|
||||
我们这里投机取巧一下,利用 KubeSphere 的图形化操作一波,这样可以保证部署的一次成功率 (还有一个隐藏的好处,先卖个关子)。
|
||||
|
||||
使用**企业空间管理员**权限的账户,登录 KubeSphere 控制台。
|
||||
|
||||
**这一步没有使用 admin 用户,采用多租户户形式,模拟真实的生产环境**
|
||||
|
||||
<,>
|
||||
|
||||
点击**项目**,点击 **lstack** 项目,进入项目的管理页面 (如无特殊说明,后面的很多界面操作都是在该页面完成)。
|
||||
|
||||
<,>
|
||||
|
||||
**应用负载**->**工作负载**->**有状态副本集**,点击**创建**。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
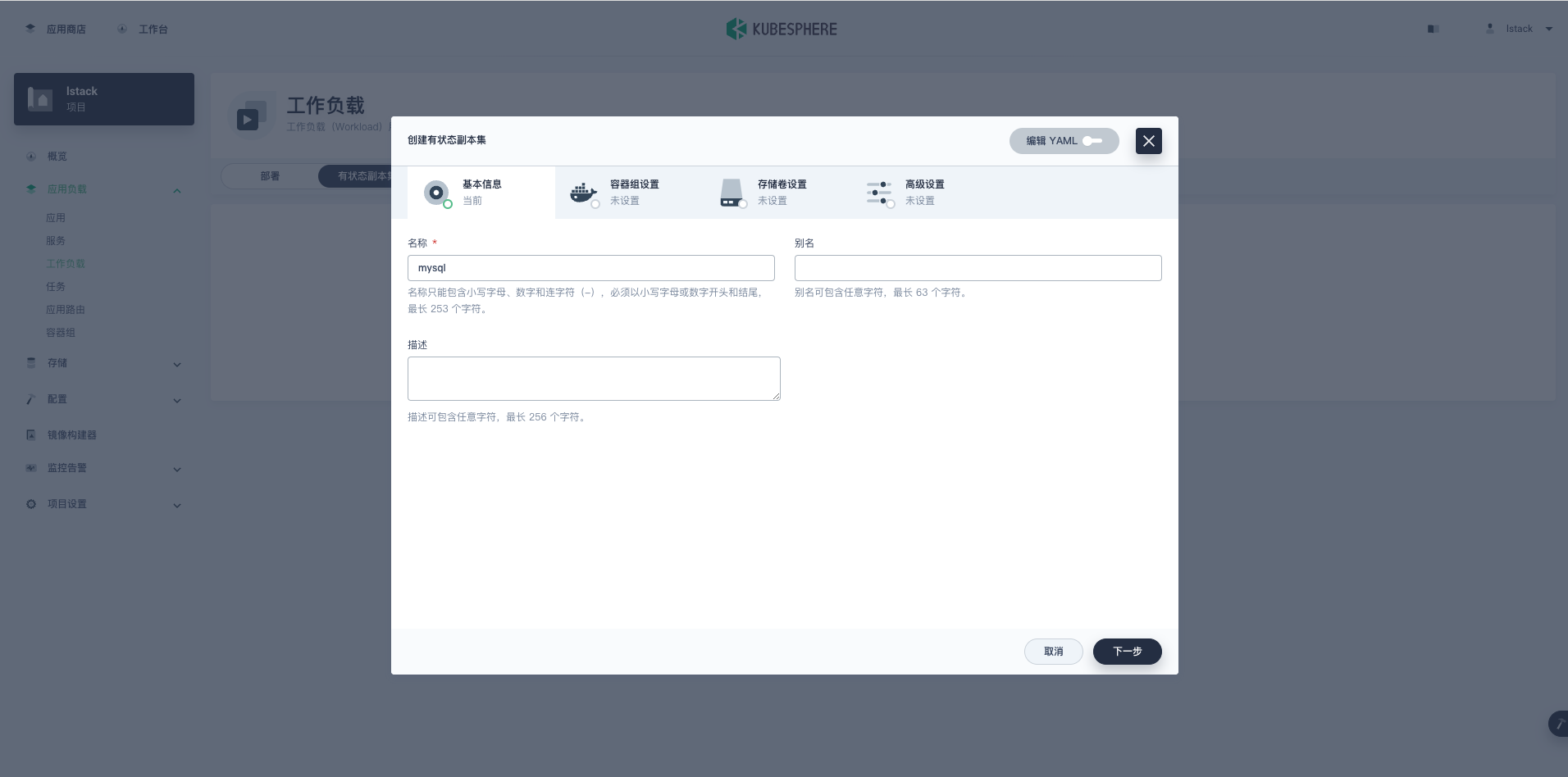
弹出**创建有状态副本集**页面,**基本信息**页,**名称**输入 **mysql**。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
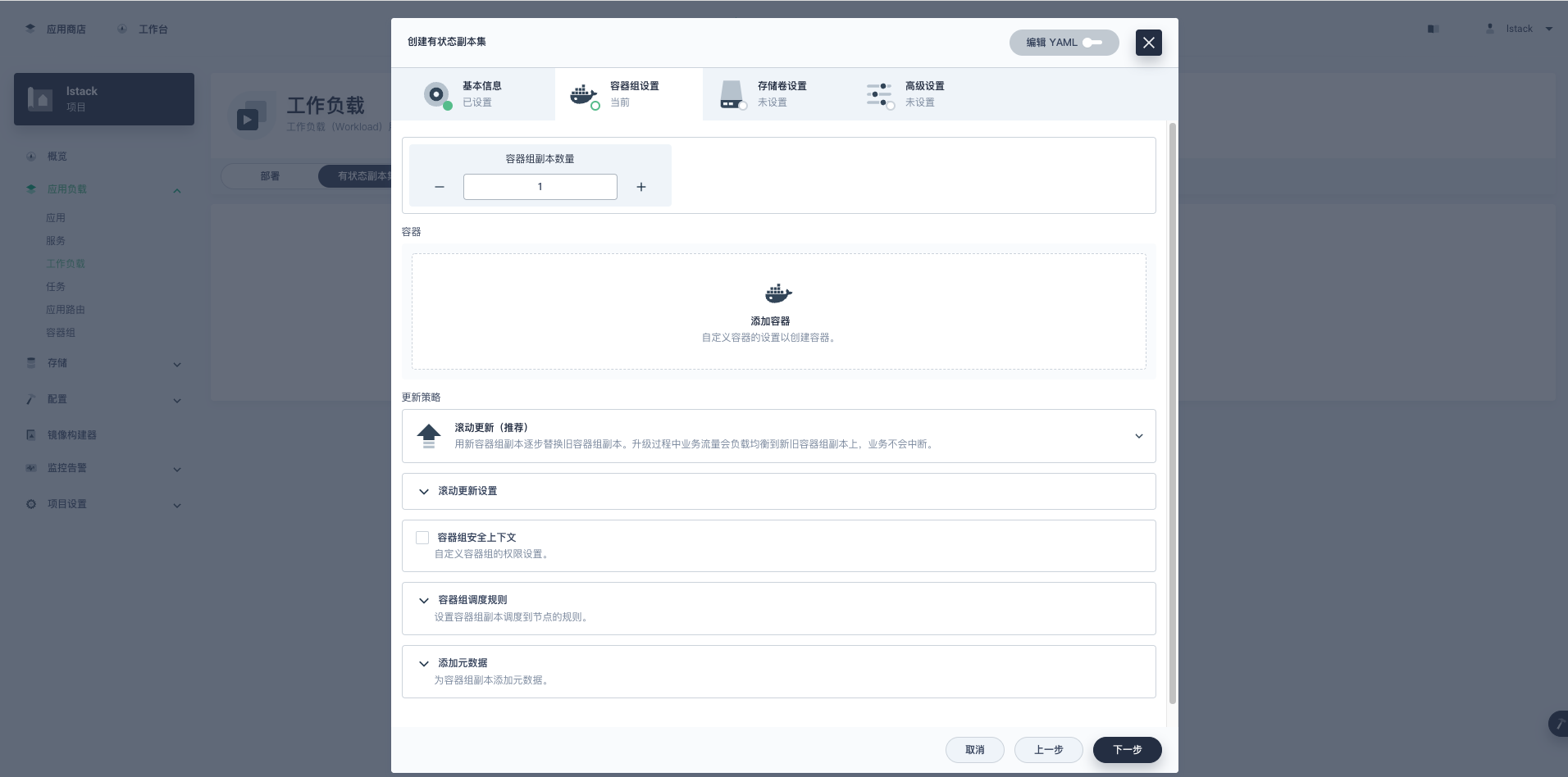
**容器组设置**页。
|
||||
|
||||
- **容器组副本数量**:1
|
||||
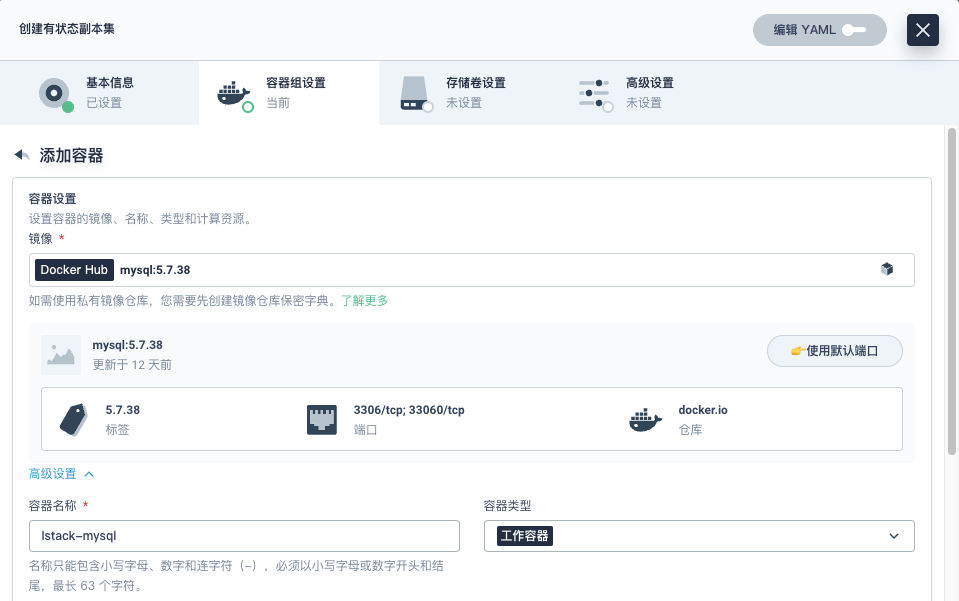
- 点击**添加容器**,镜像搜索栏输入 **mysql:5.7.38**
|
||||
- **容器名称**: lstack-mysql
|
||||
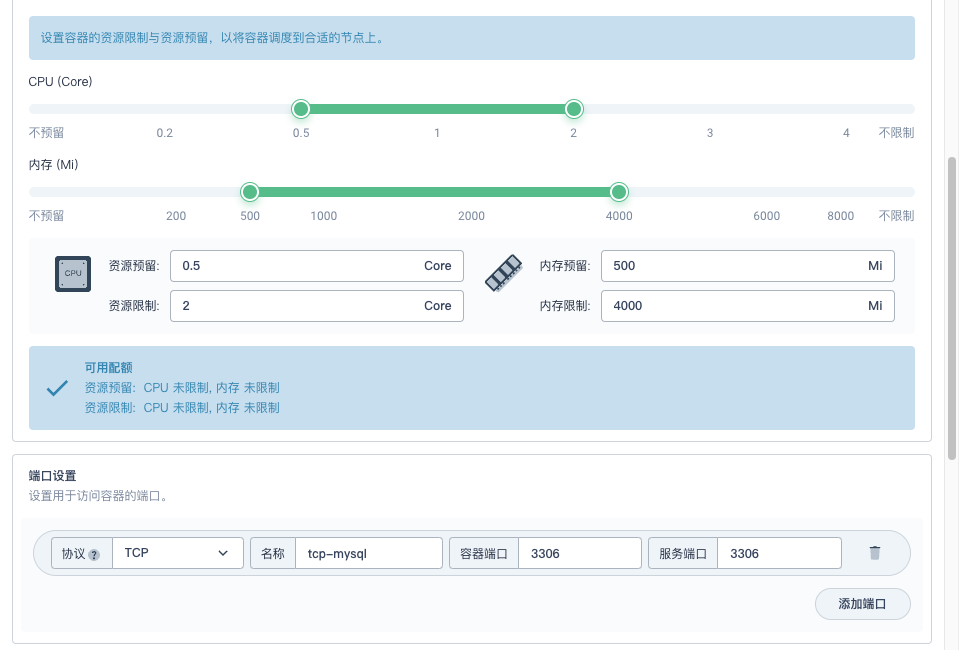
- **CPU(Core)资源**:预留 0.5,限制 2
|
||||
- **内存(Mi)**:预留 500i,限制 4000
|
||||
- **端口设置**:协议 TCP,名称 tcp-mysql,容器端口:3306,服务端口 3306
|
||||
- **环境变量**:
|
||||
- 引用配置字典或保密字典
|
||||
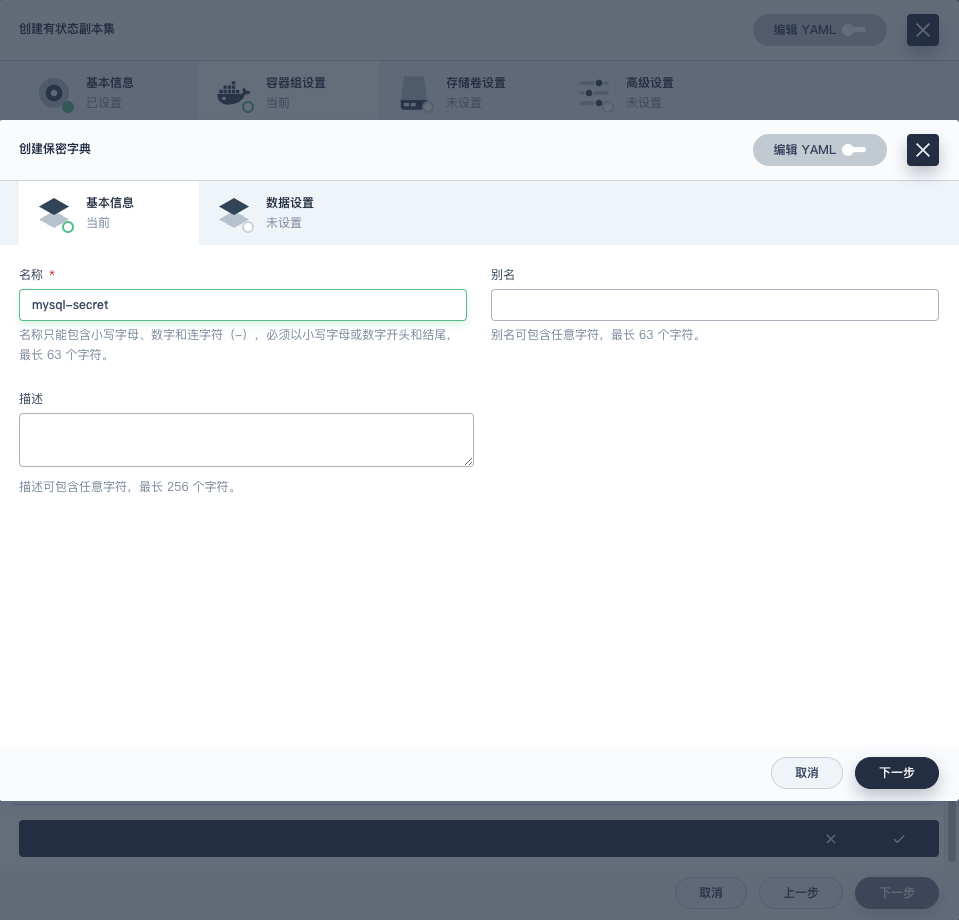
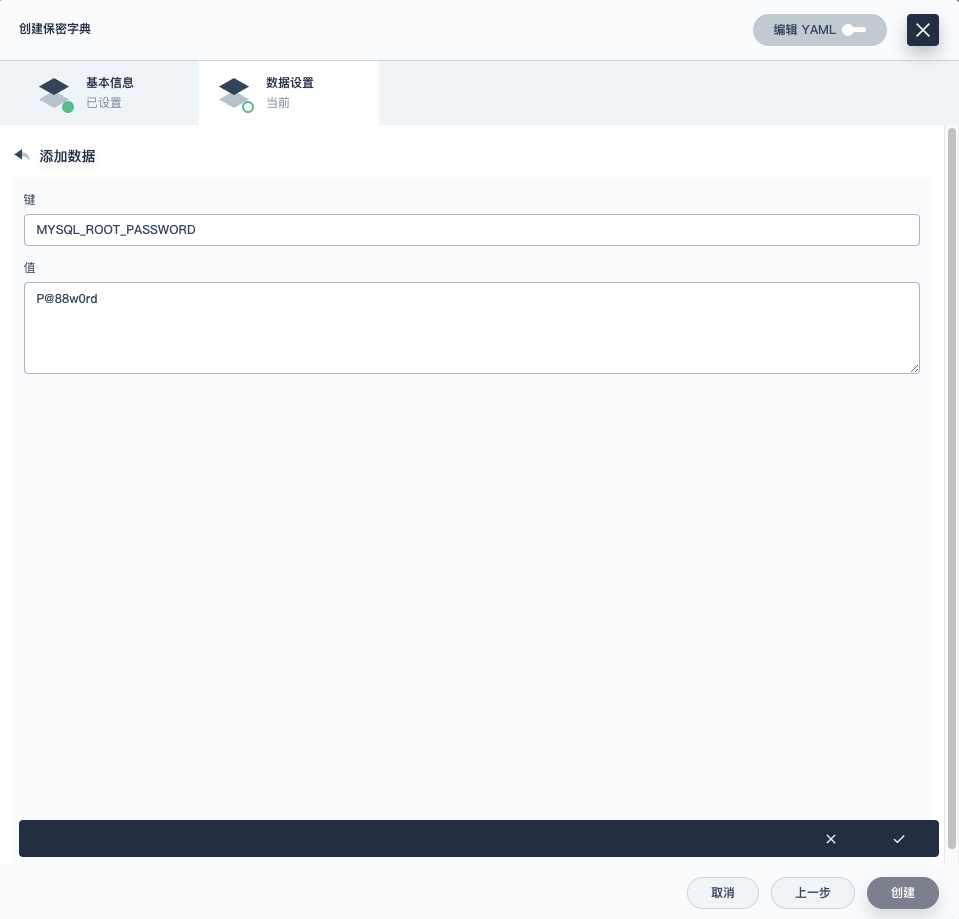
- 创建保密字典,键(MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD),值(P@88w0rd)
|
||||
- **同步主机时区**:勾选上
|
||||
- 其他未说明的配置采用默认值
|
||||
|
||||
<,,,>
|
||||
|
||||
**创建保密字典**:在**环境变量**选项中,点击**创建保密字典**,按后续图示操作。
|
||||
|
||||
<,,,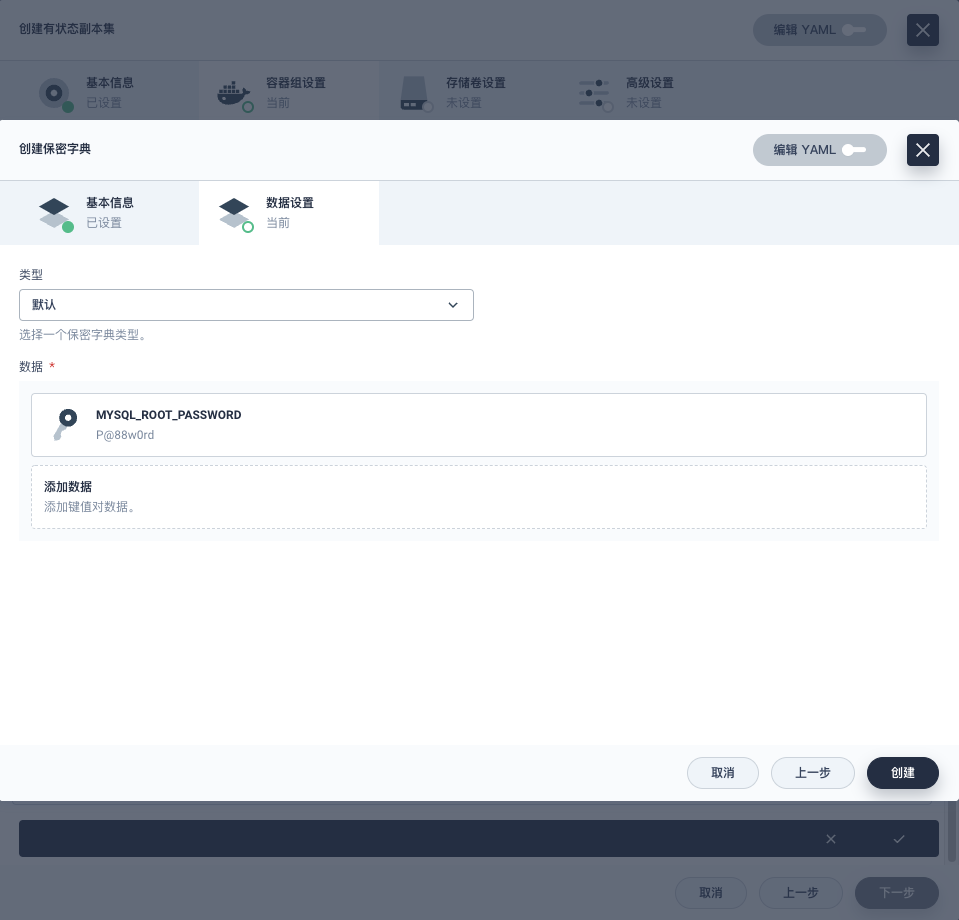>
|
||||
|
||||
点击**创建**,返回**容器组设置**页面。
|
||||
|
||||
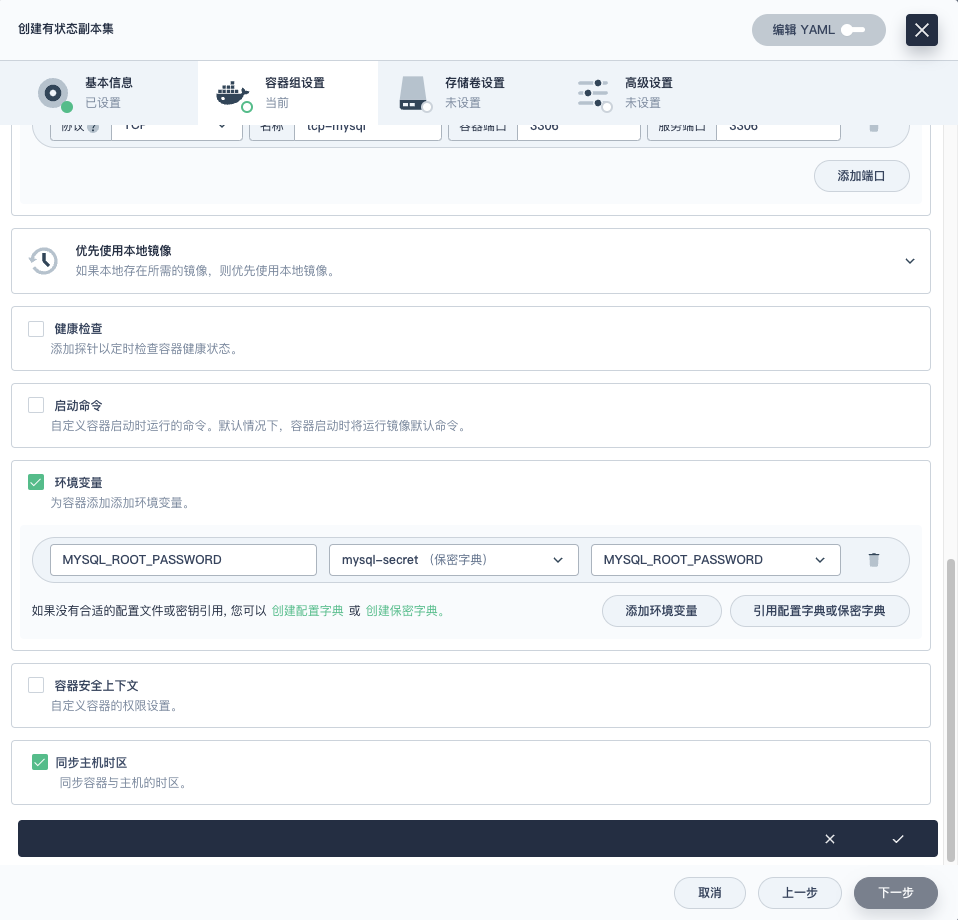
|
||||
|
||||
按以上信息配置完成后,点击**对号**按钮。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**容器组设置**完成后,点击**下一步**,进入**存储卷设置**。
|
||||
|
||||
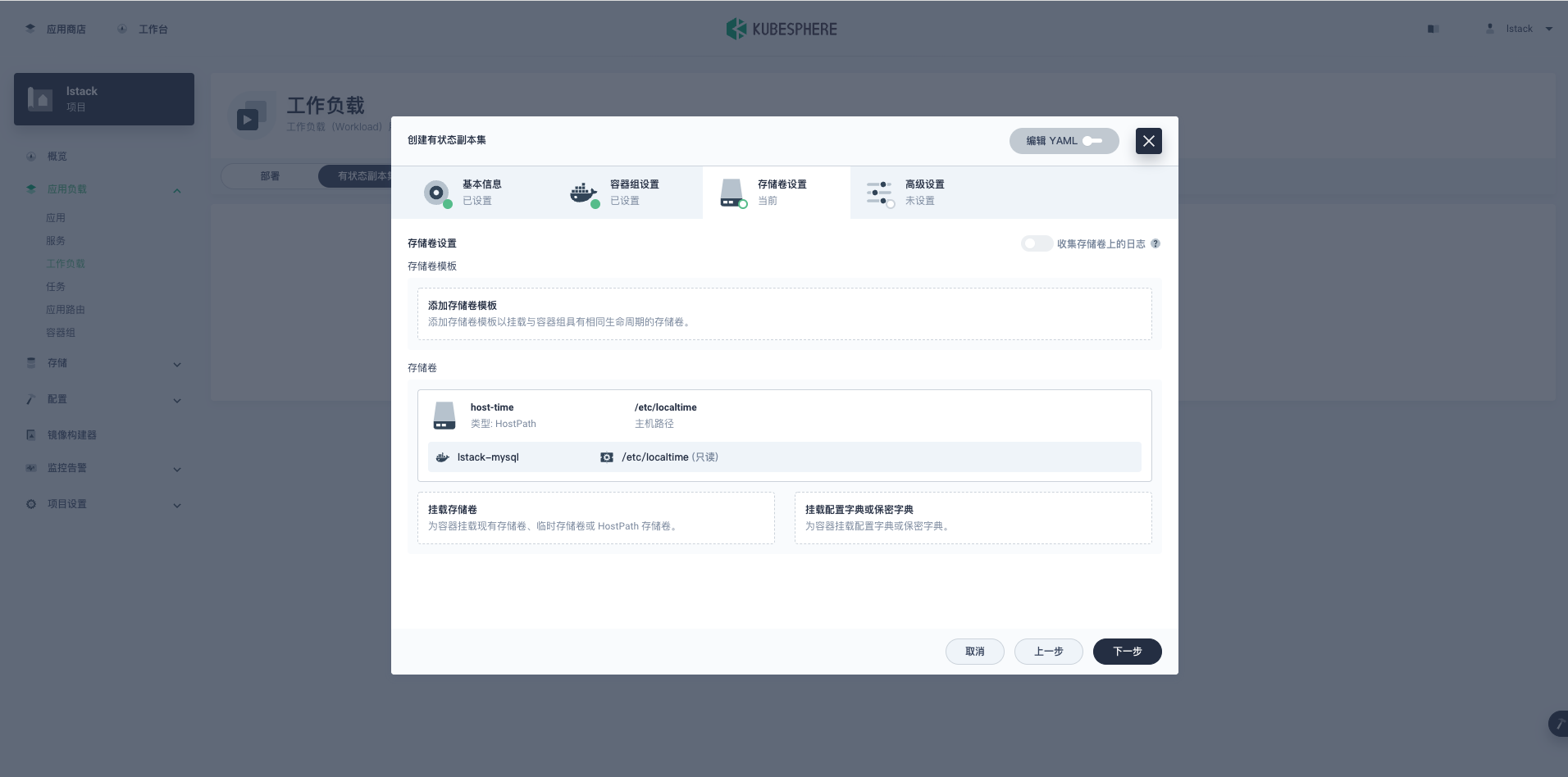
|
||||
|
||||
**存储卷设置**->**存储卷模板**->**添加存储卷模板**。
|
||||
|
||||
- 存储卷名称:data
|
||||
- 这个地方不要多写,系统会自动添加 StatefulSet 的名称作为名称后缀,生成类似 data-mysql-0 命名形式的存储卷
|
||||
- 存储类型:glusterfs
|
||||
- 访问模式:ReadWriteOnce
|
||||
- 存储卷容量:5Gi
|
||||
- 挂载路径:读写 /var/lib/mysql
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
按以上信息配置完成后,点击**对号**按钮。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**存储卷设置**完成后,点击**下一步**,进入**高级设置**,保持默认值,点击**创建**按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
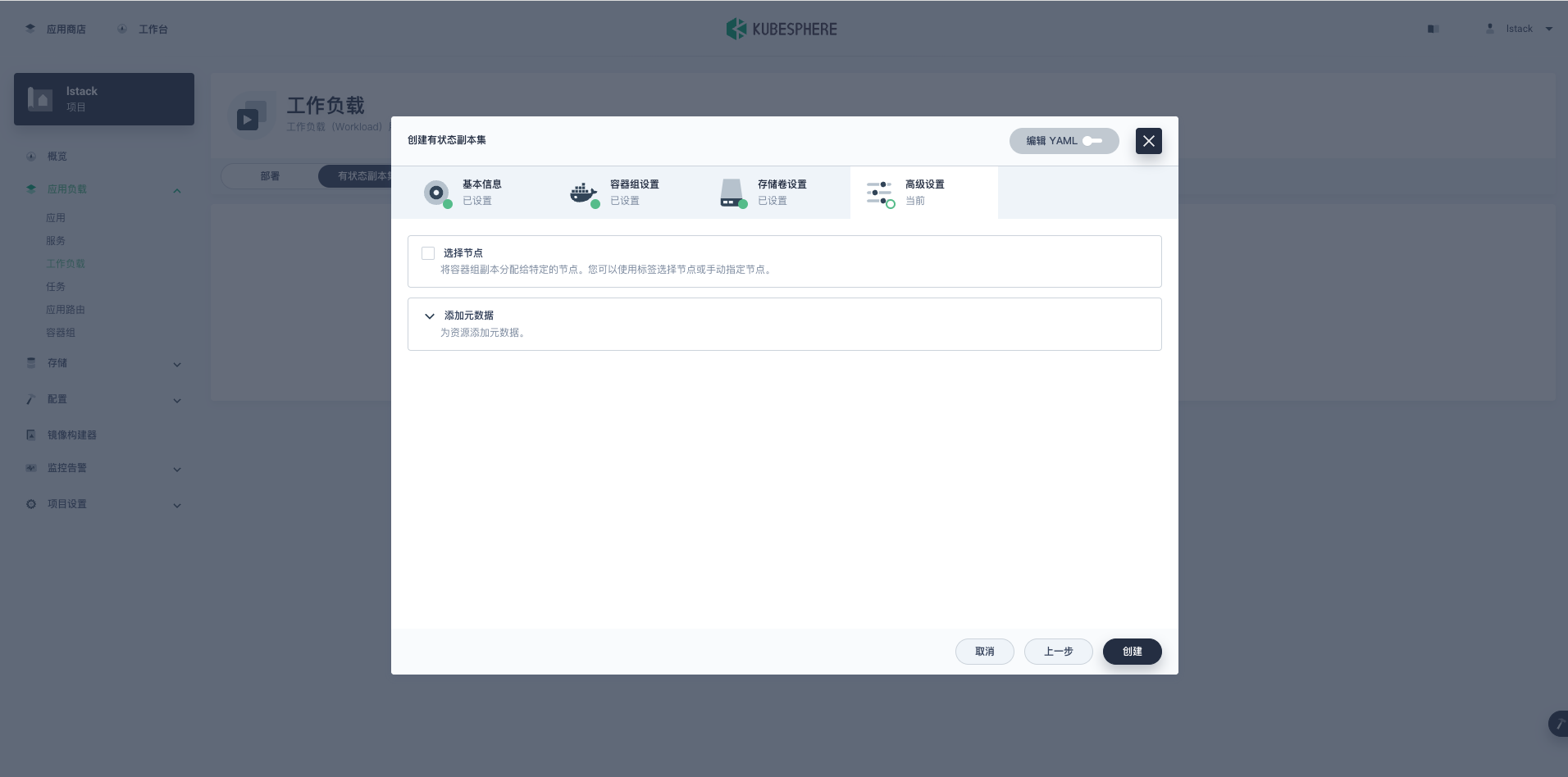
|
||||
|
||||
**创建**成功后,自动返回工作负载页面。第一次创建会去 DockerHub 下载镜像,所以初始显示状态为**更新中**。
|
||||
|
||||
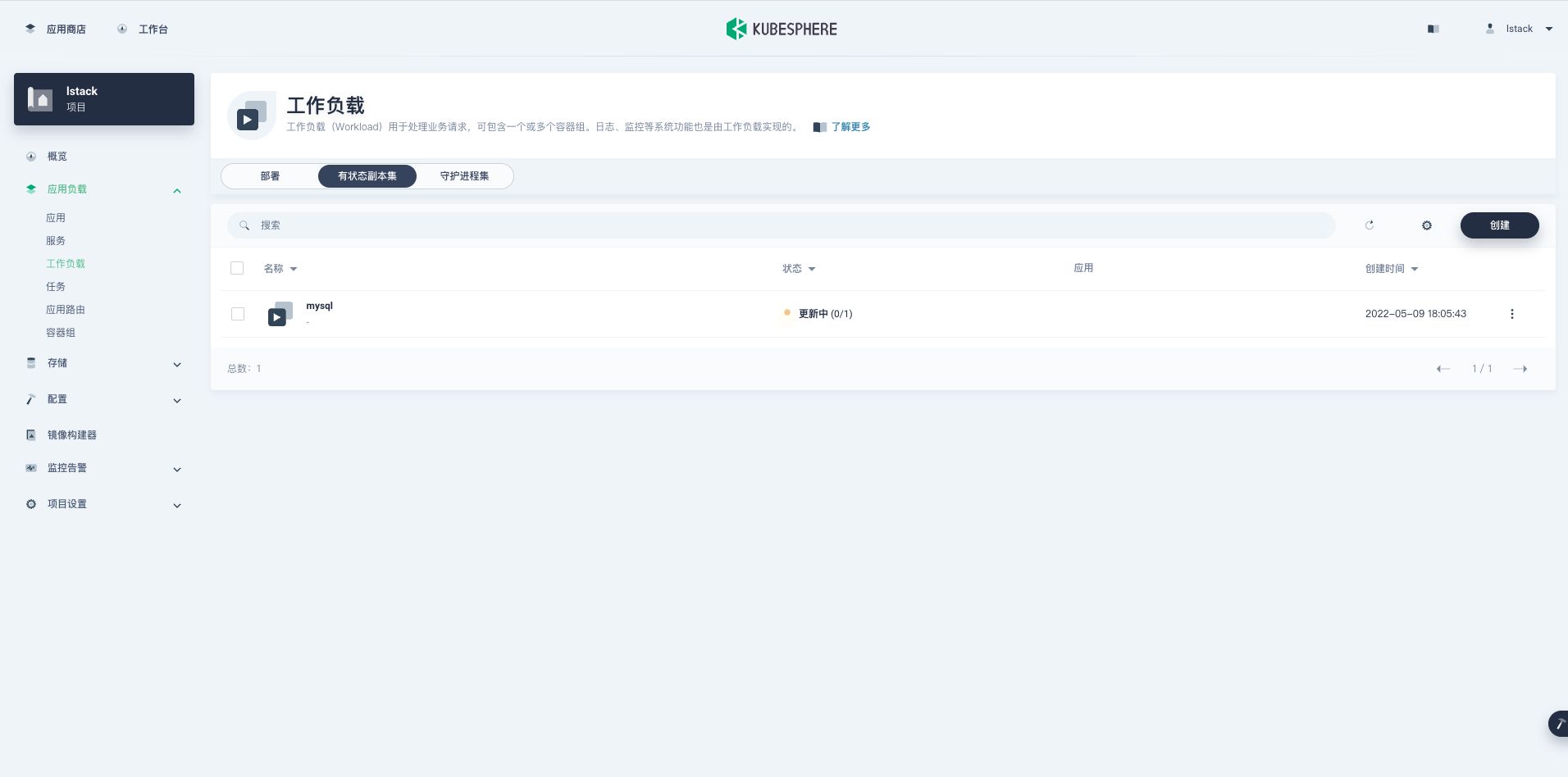
|
||||
|
||||
镜像下载完成并且容器配置正确时,状态变成**运行中**。
|
||||
|
||||
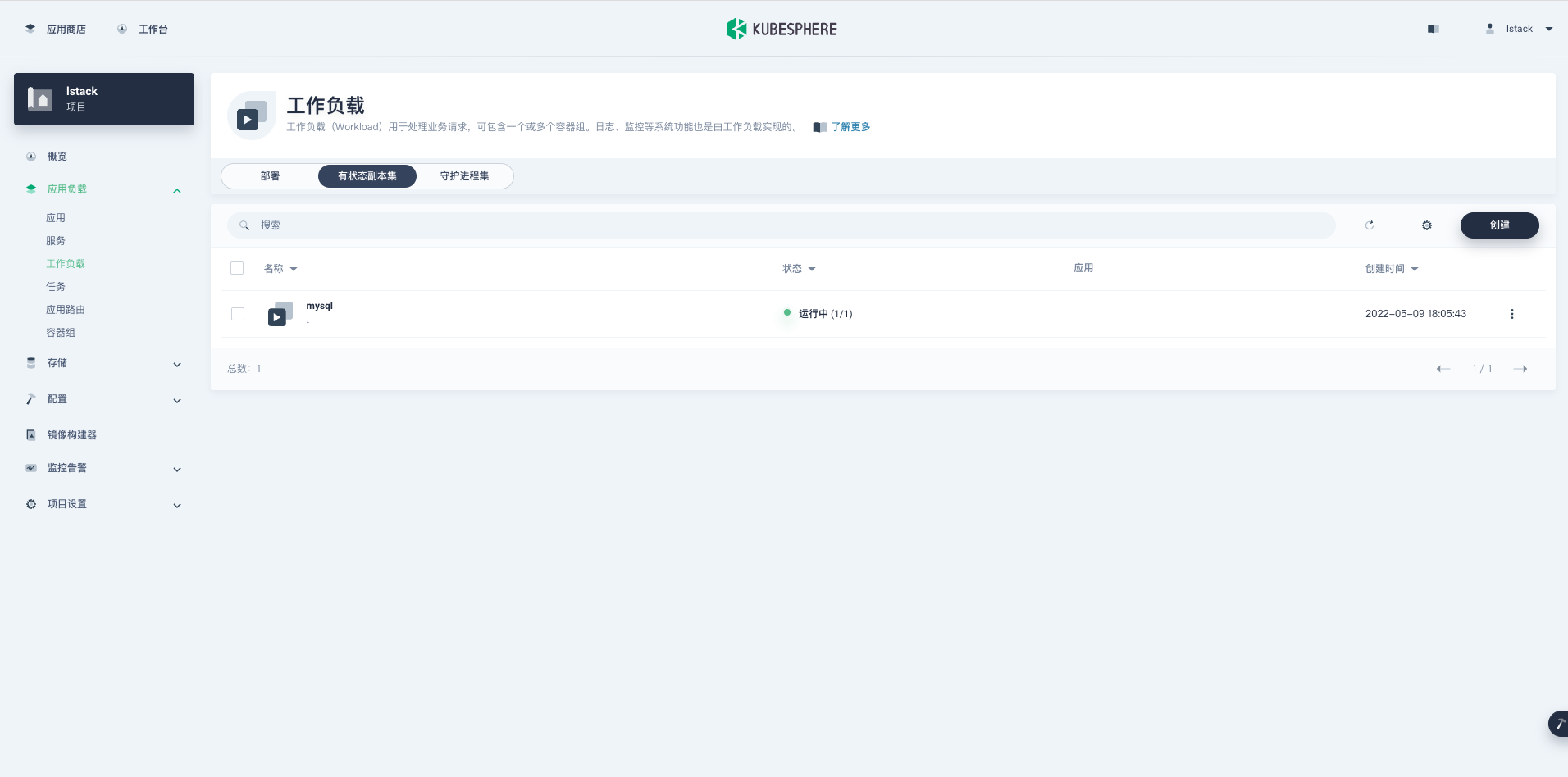
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **mysql**,进入有状态副本集详细页面。
|
||||
|
||||
<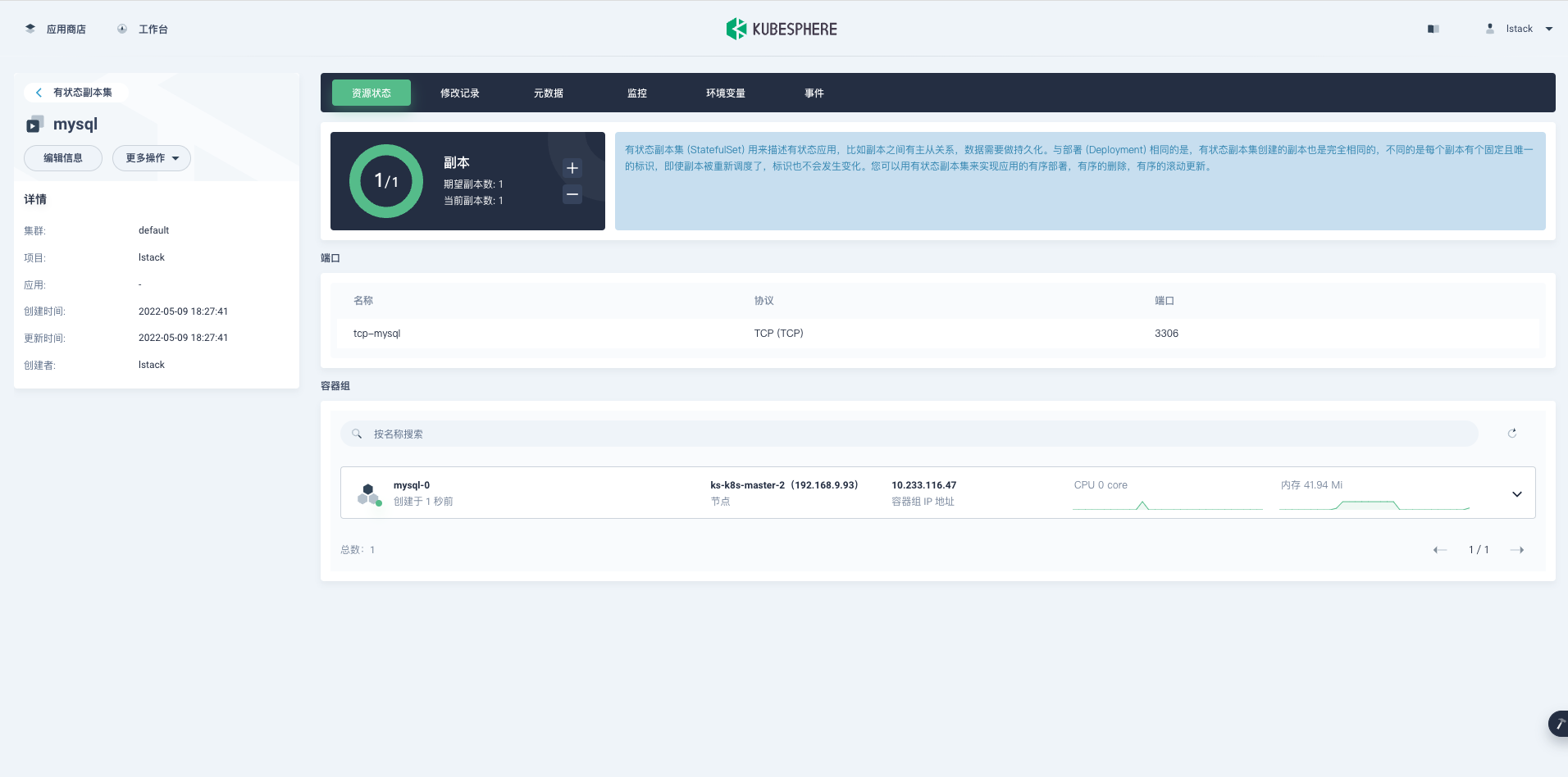,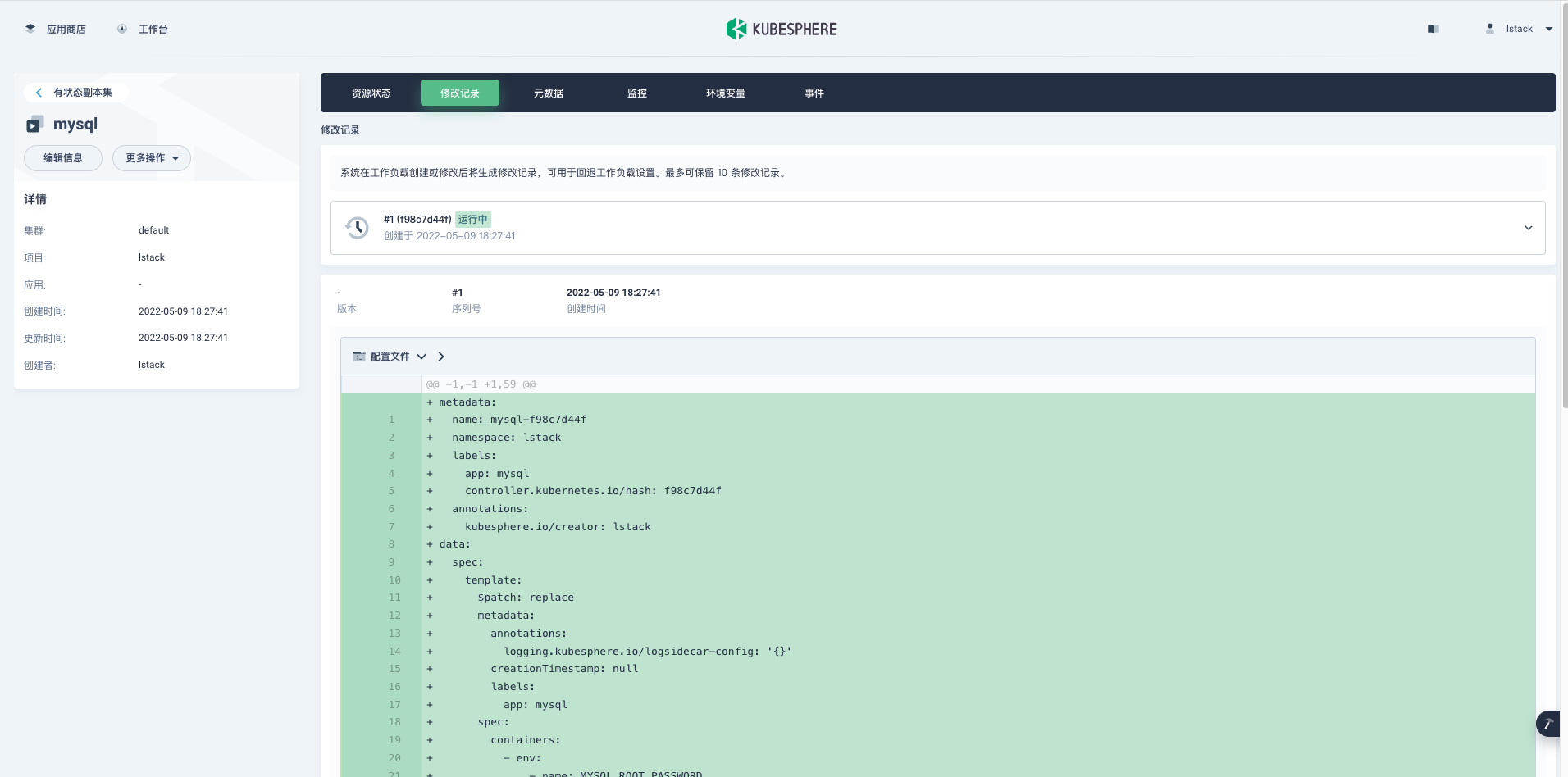,>
|
||||
|
||||
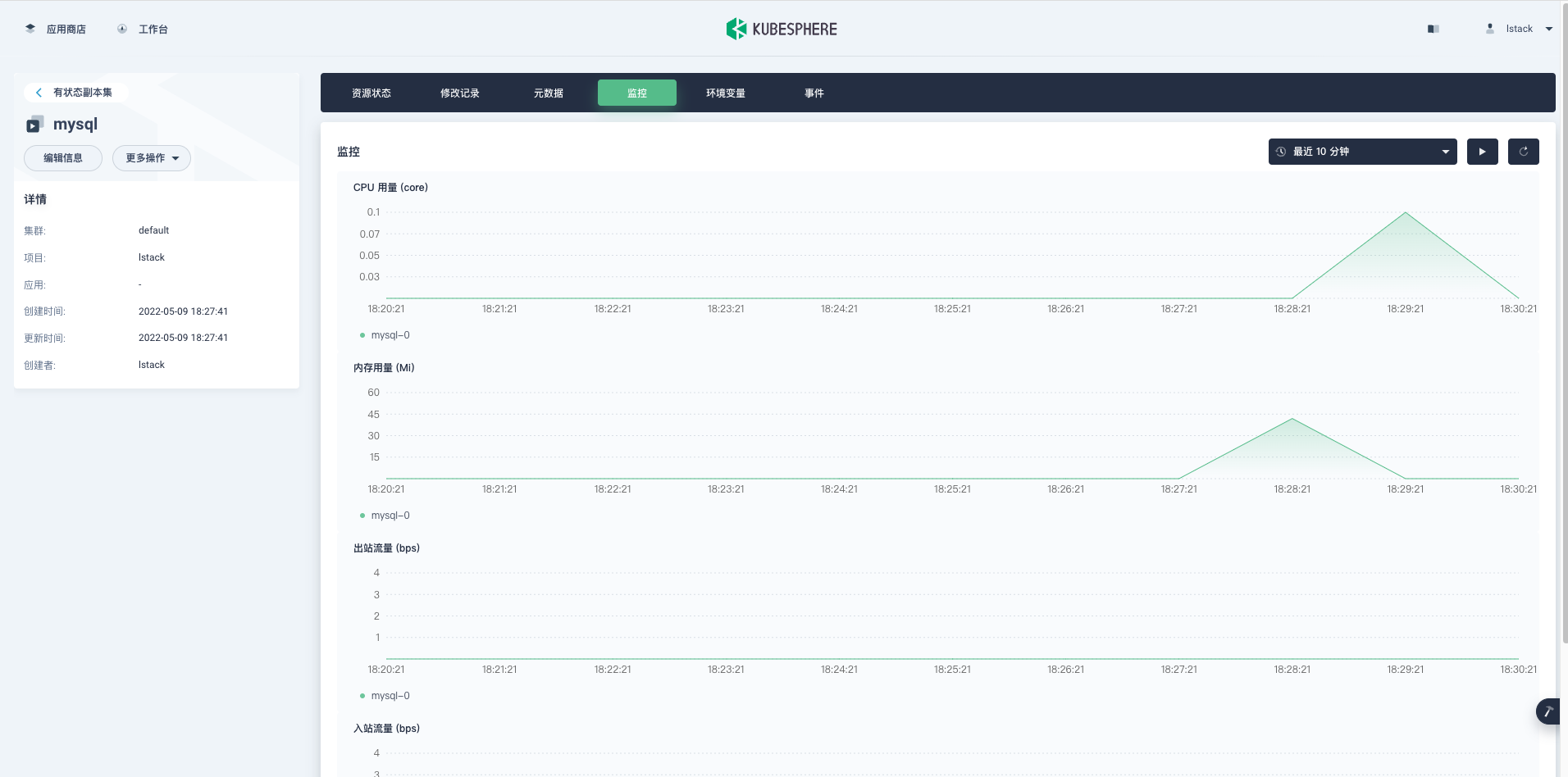
**监控**,可以看到初始启动时的资源使用情况,后续可以根据监控数据调整我们的资源的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
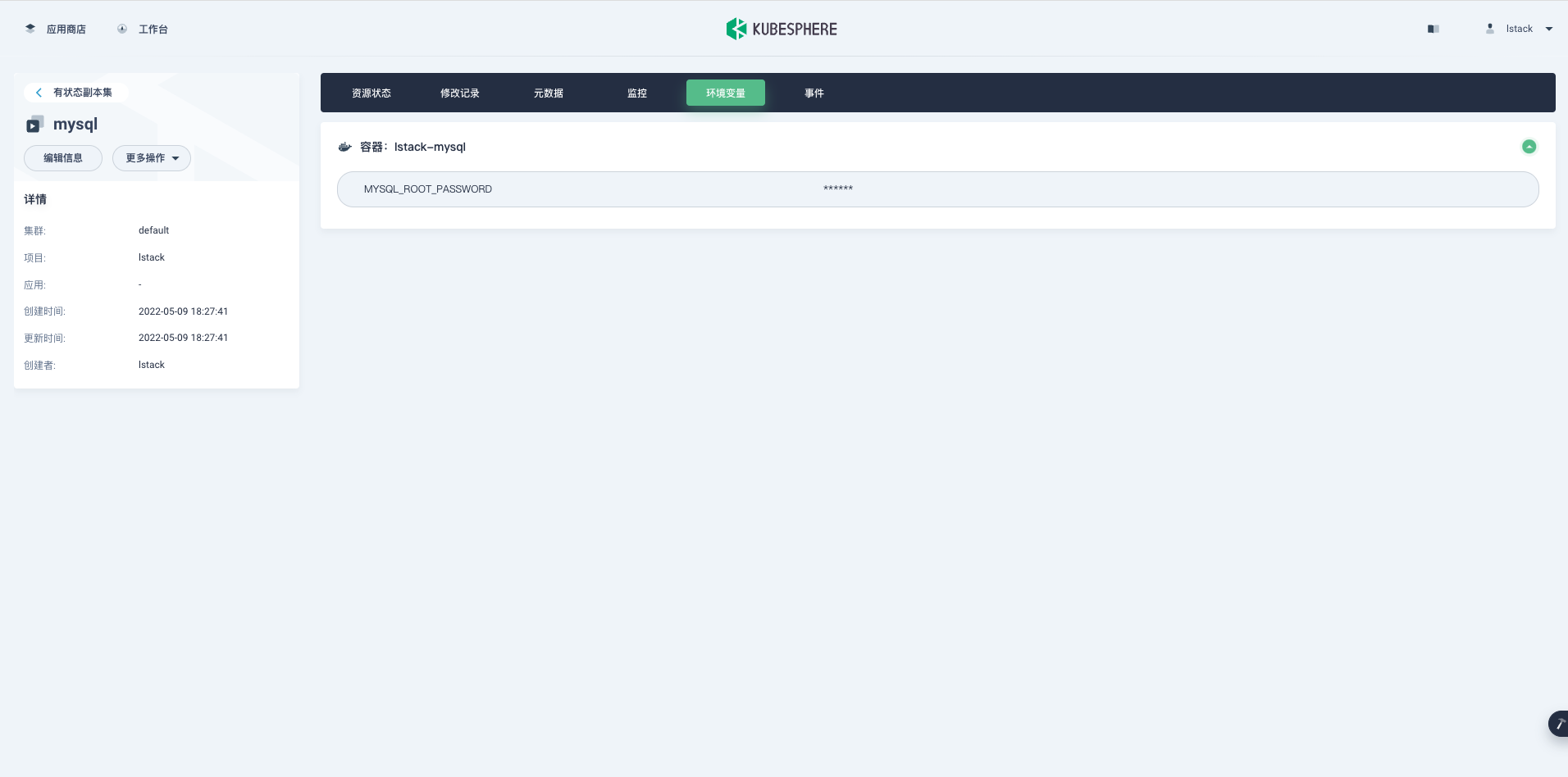
**环境变量**,可以看到我们新增加的 Secret 字典生效了,并且密码是隐藏显示的。
|
||||
|
||||
<,>
|
||||
|
||||
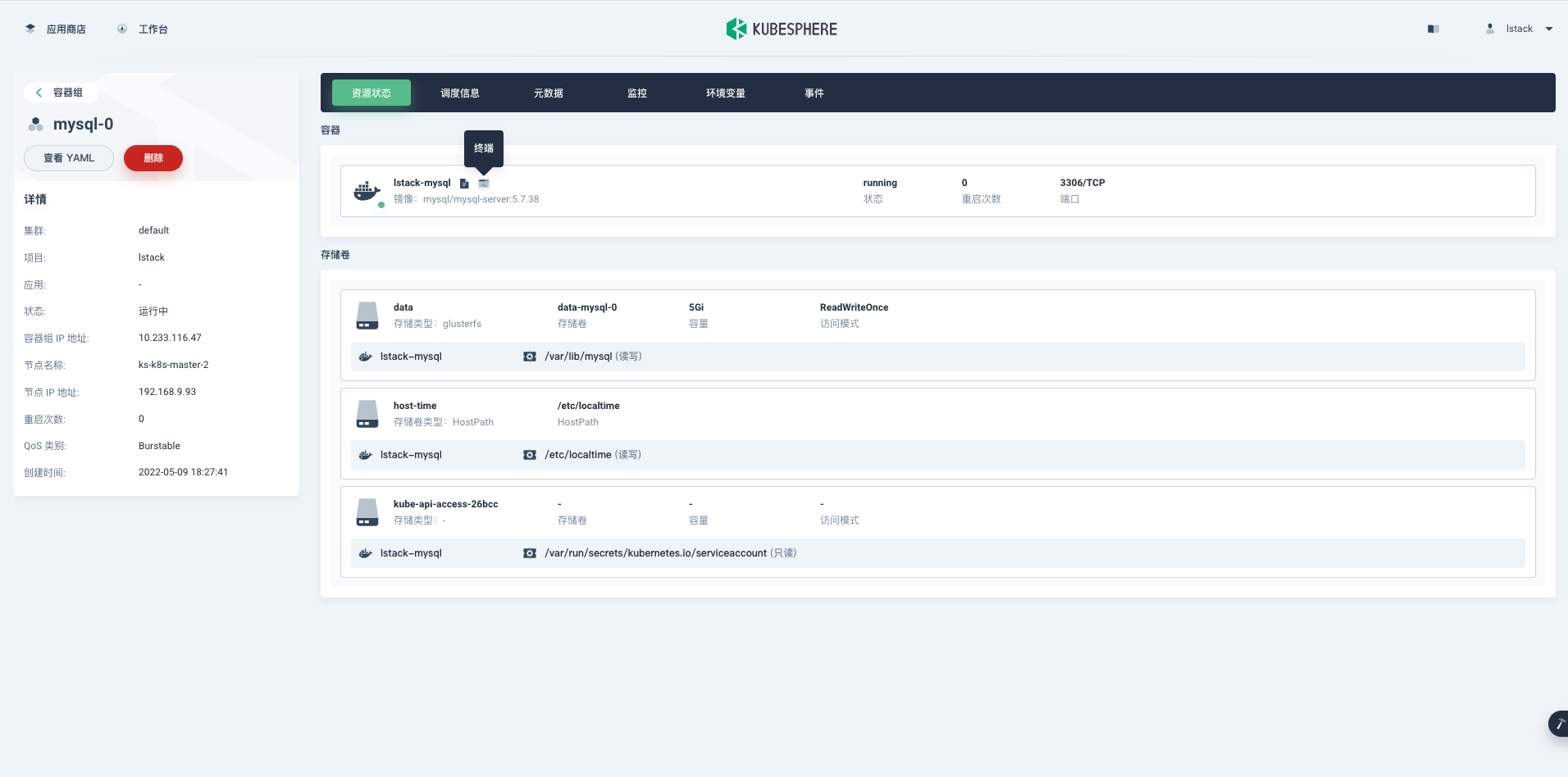
再来看看**容器组**的详细信息,在**资源状态**页面,点击容器组 **mysql-0。**
|
||||
|
||||
<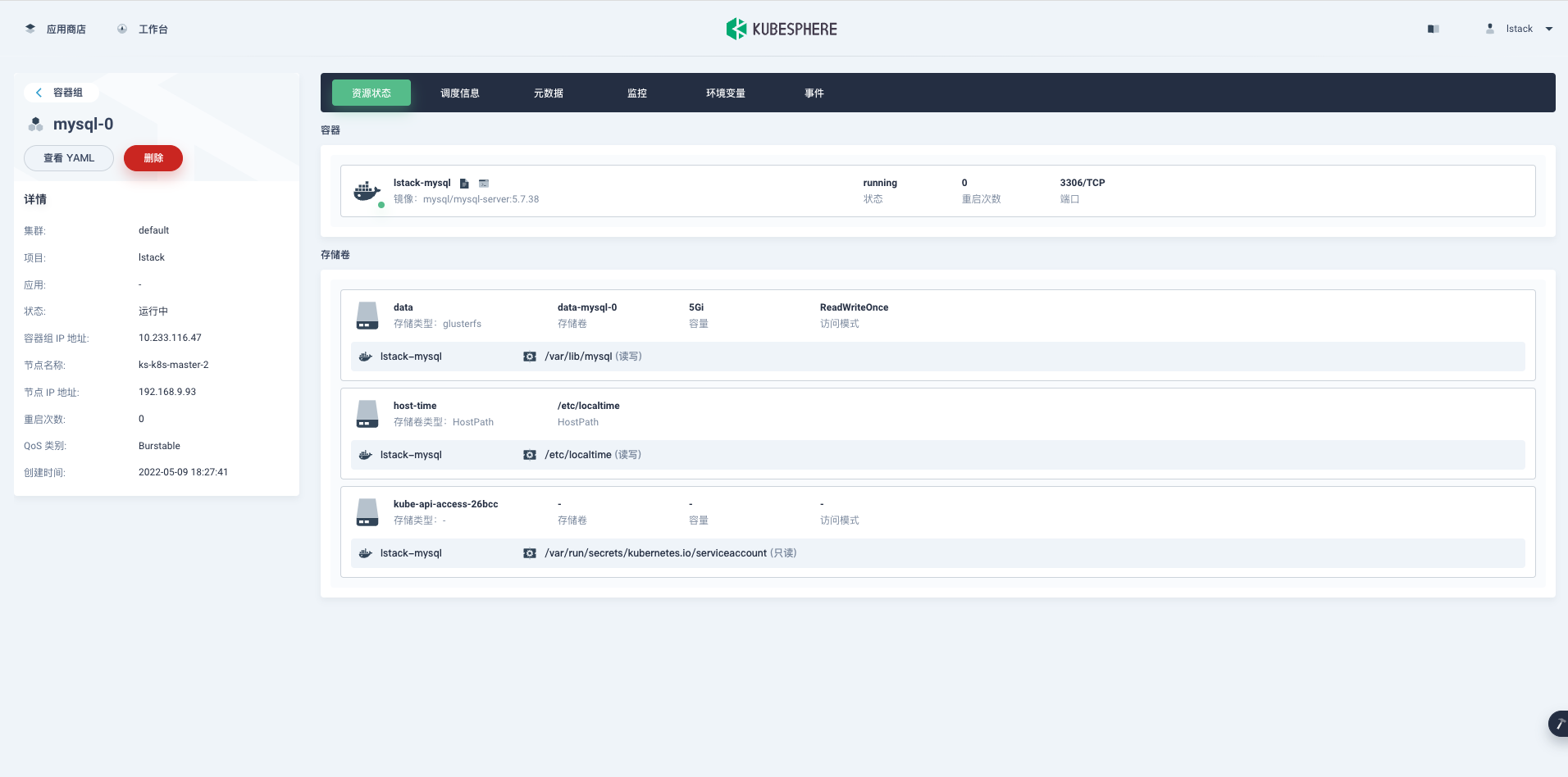,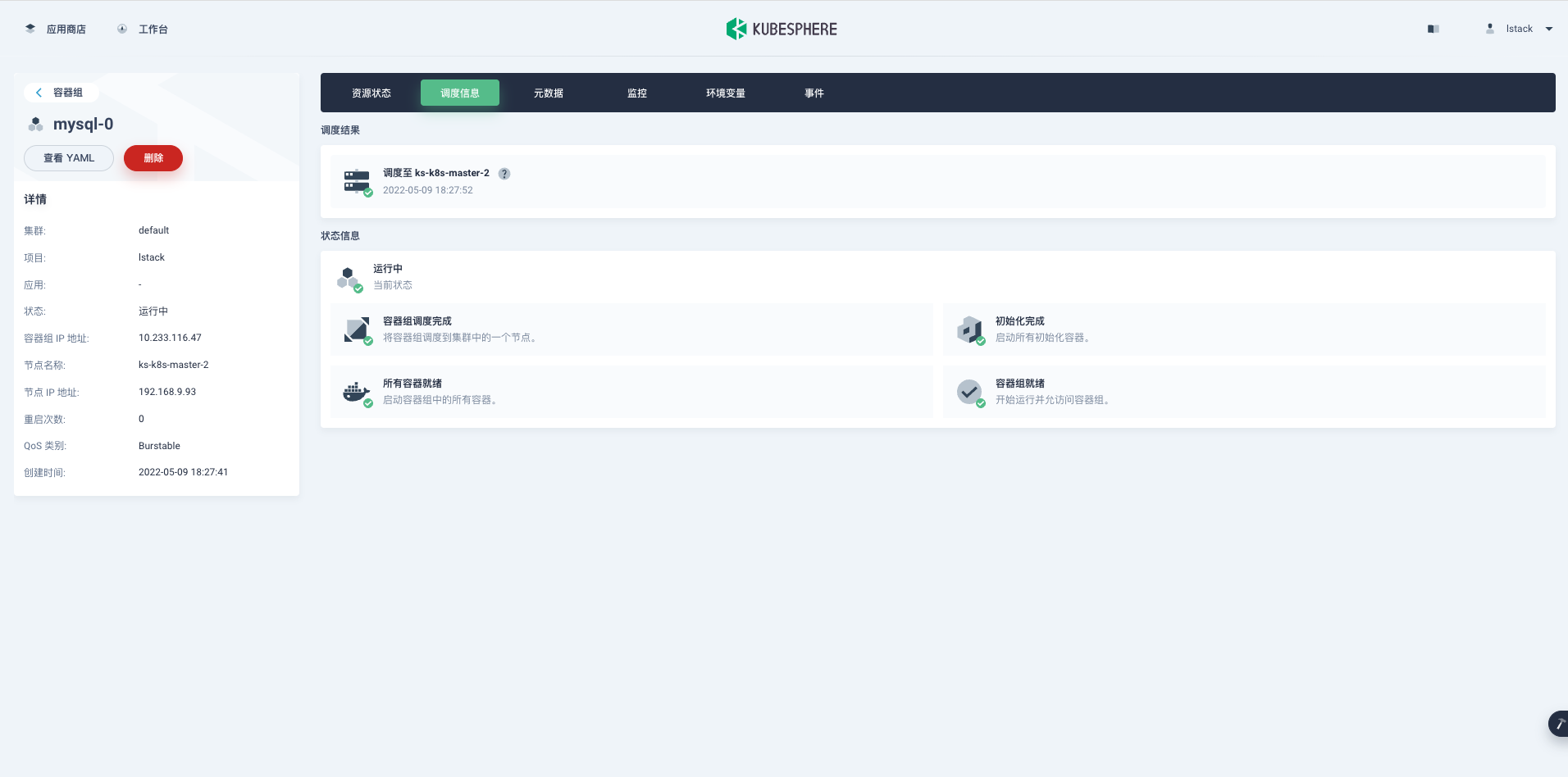,,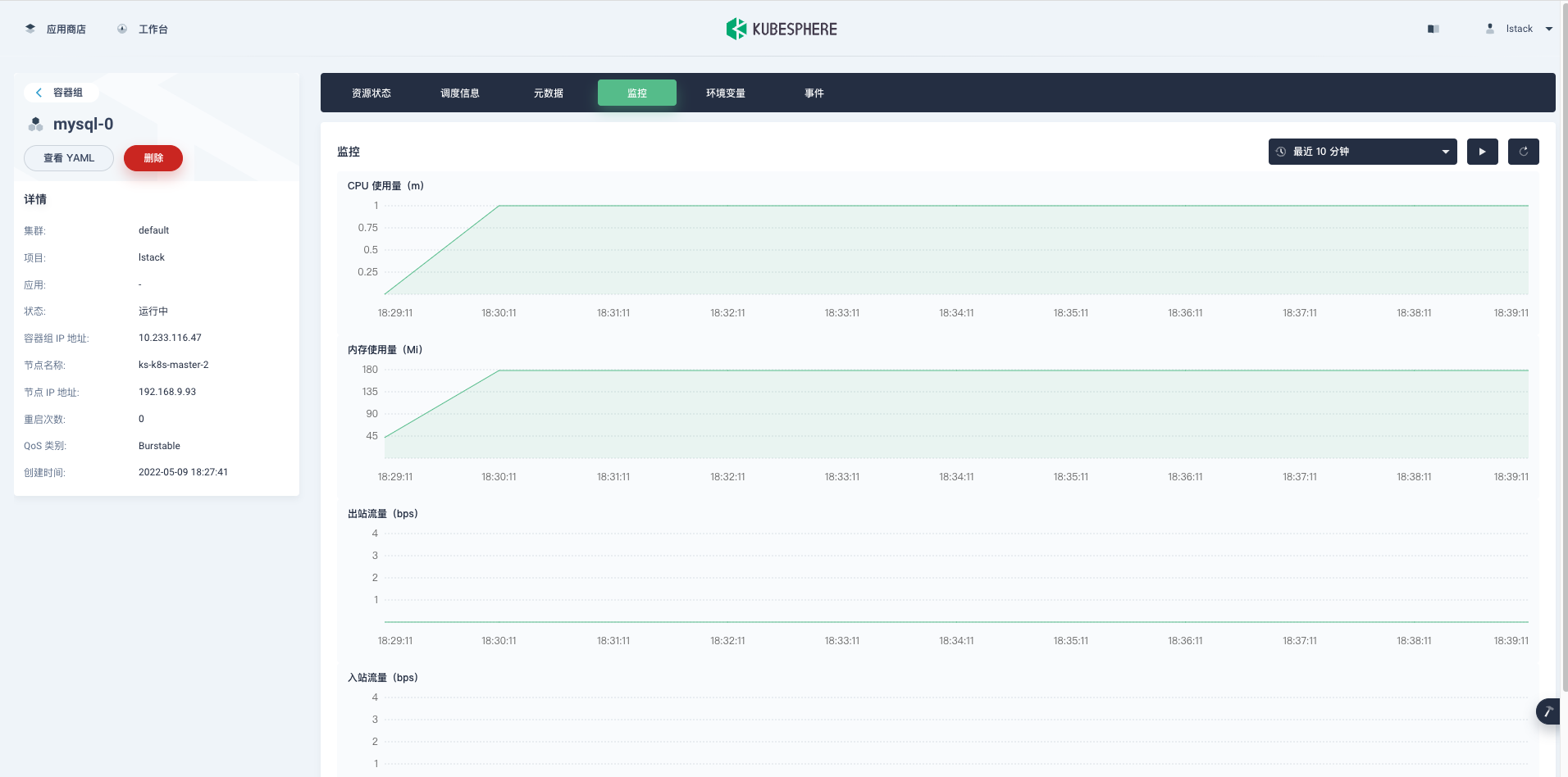,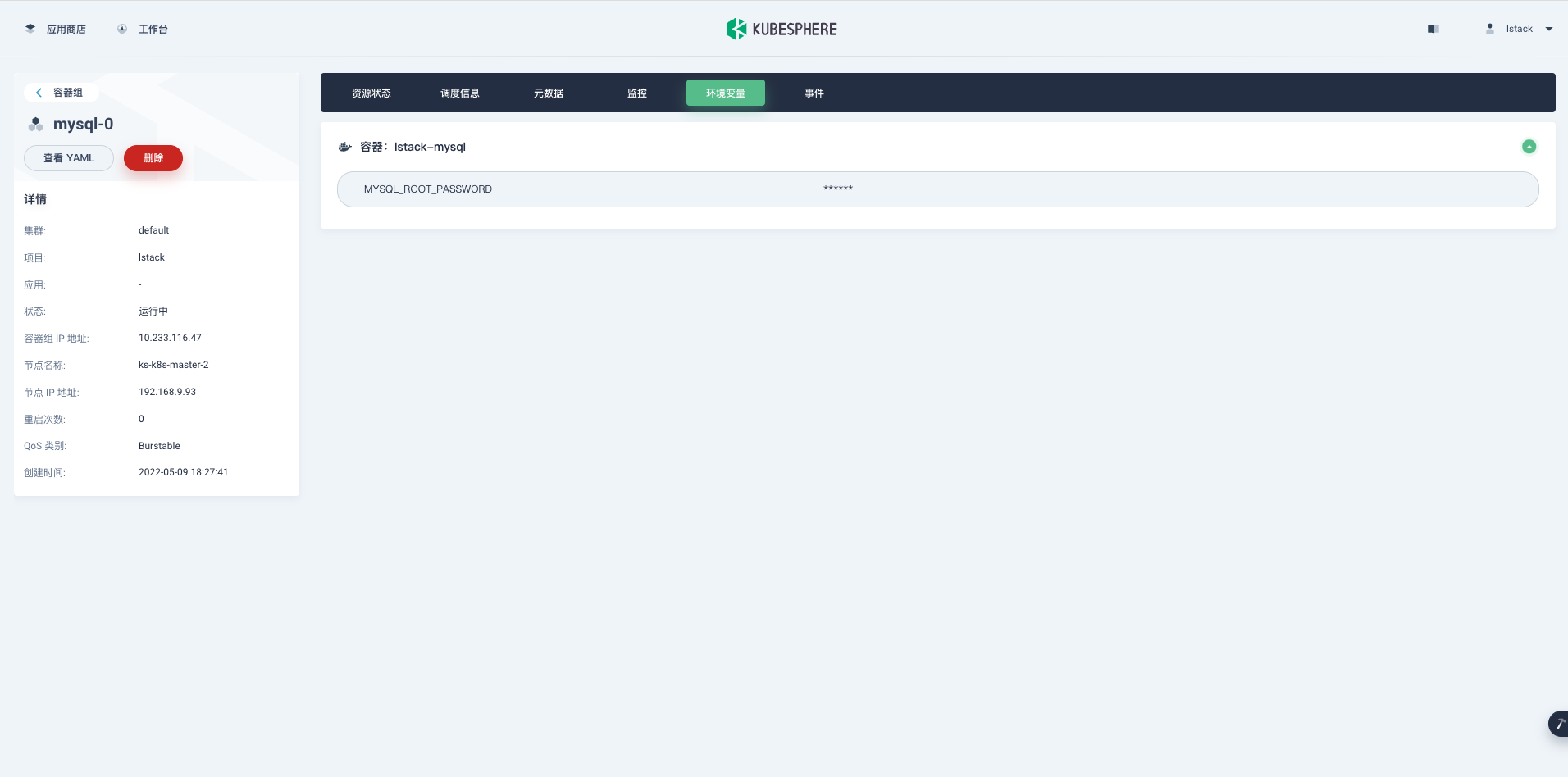,>
|
||||
|
||||
再来看看 StatefulSet 对应的服务 (Service),**应用负载**->**服务**。
|
||||
|
||||
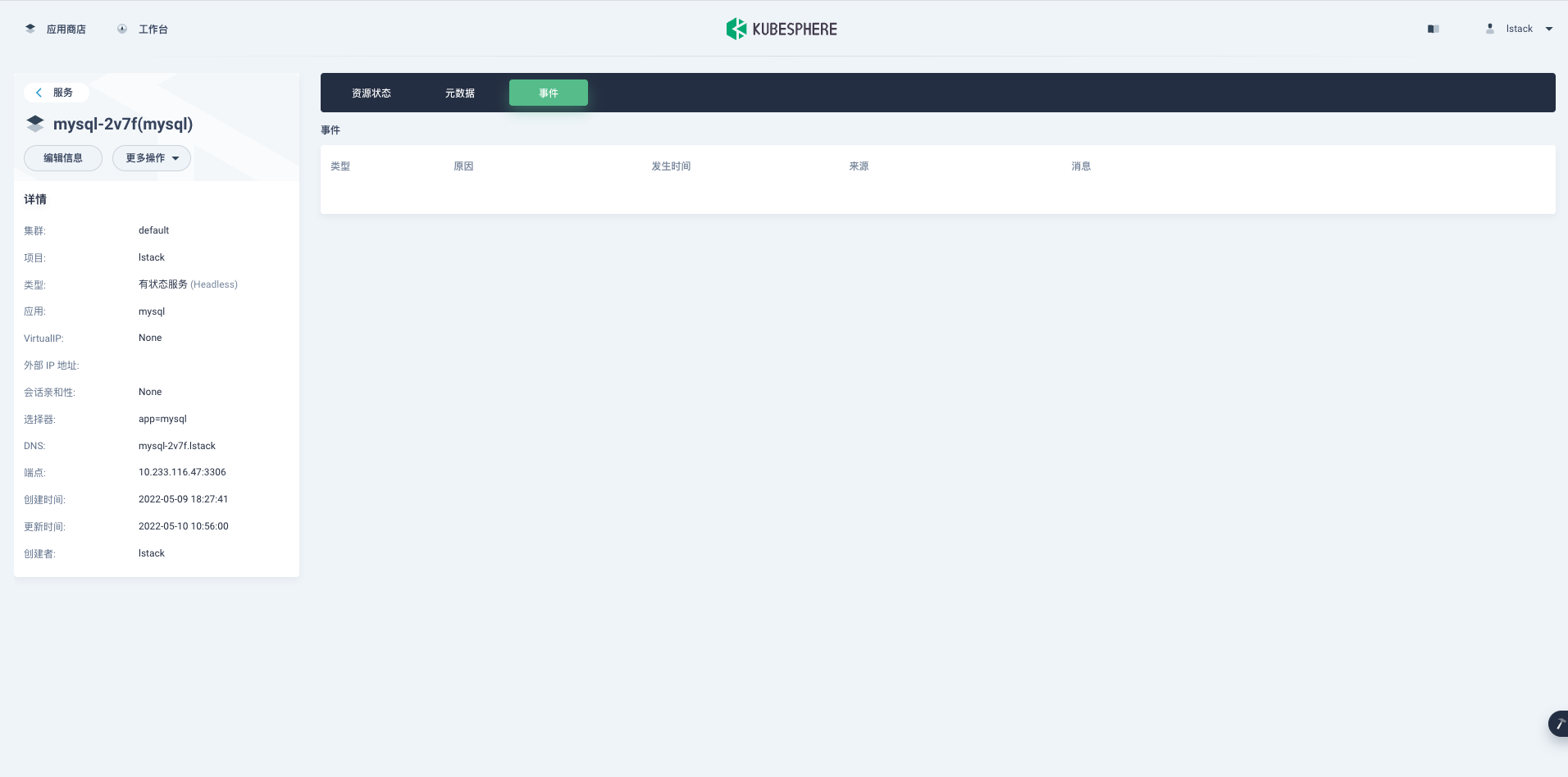
可以看到自动创建了一个 StatefulSet MySQL 对应的有状态服务 (Headless),**mysql-2v7f(mysql)**。
|
||||
|
||||
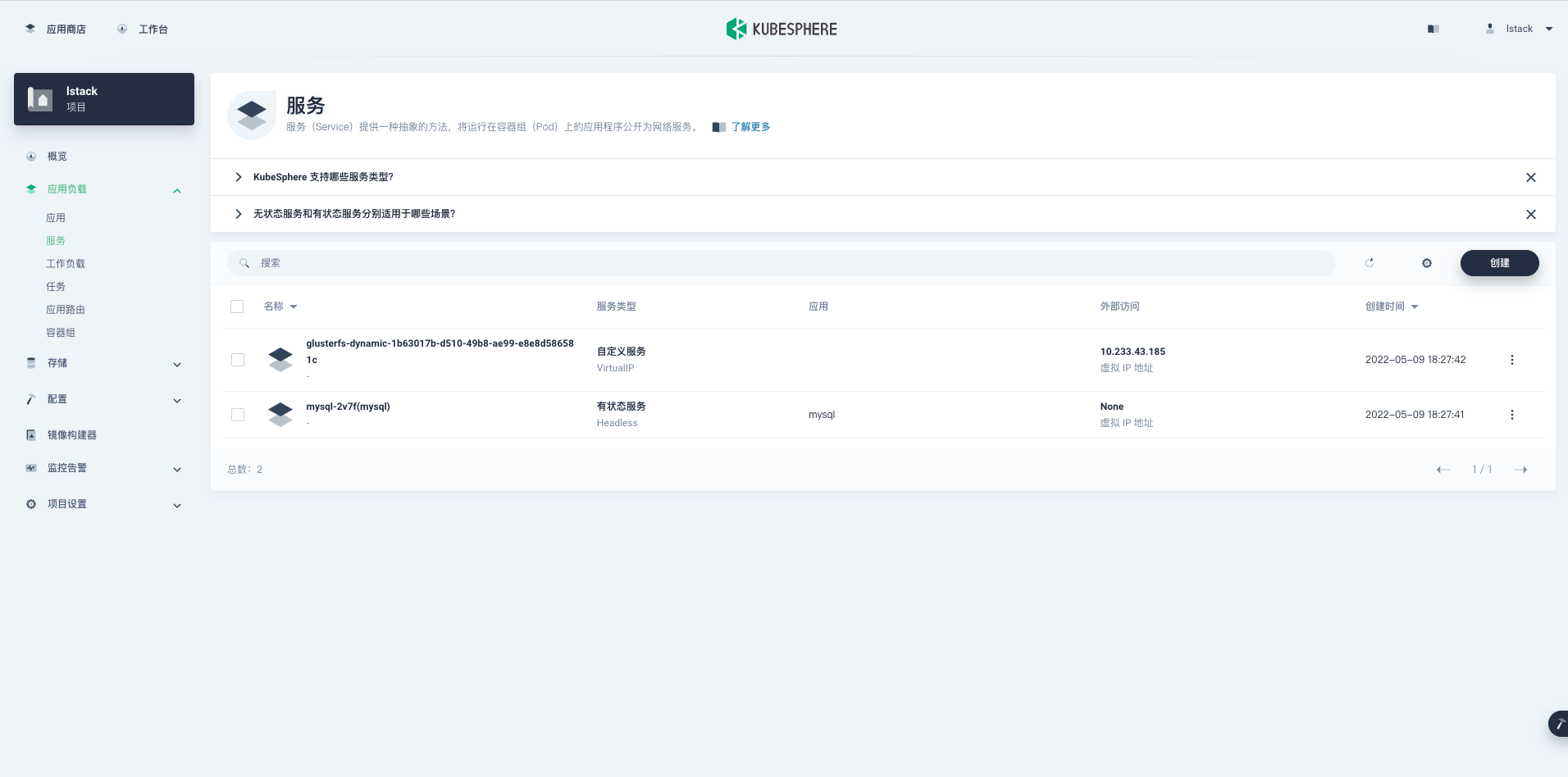
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **mysql-2v7f(mysql)**,可以查看服务详情。
|
||||
|
||||
<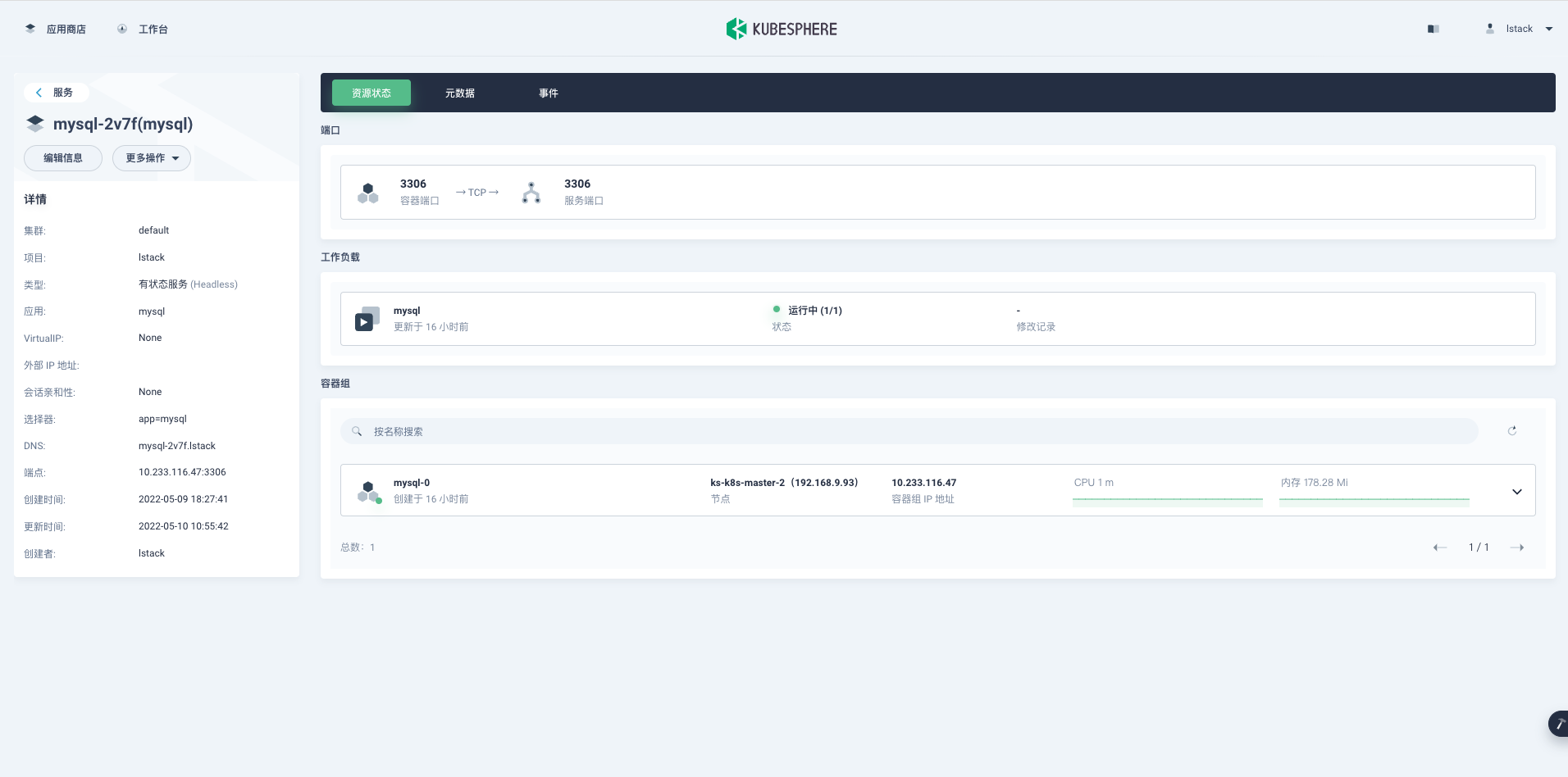,,>
|
||||
|
||||
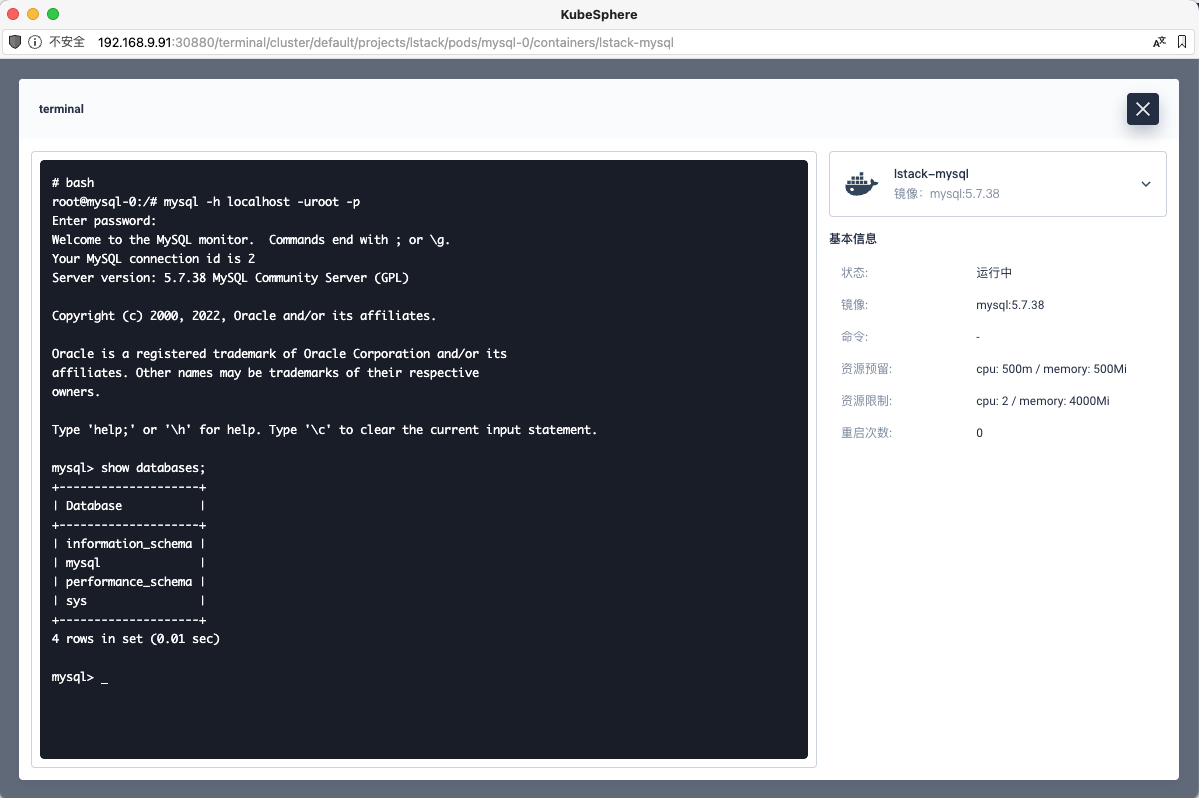
最后验证一下,我们的 MySQL 服务是否正常 (这里只看服务本身,先不测试外部连接)。
|
||||
|
||||
**应用负载**->**工作负载**->**有状态副本集**->**mysql**->**容器组**->**mysql-0**->**终端。**
|
||||
|
||||
<,>
|
||||
|
||||
至此,MySQL 在 K8s 的基本安装就完成了,K8s 集群内的其他应用可以通过 svc 的地址访问 MySQL 服务 (svc 地址就是 **mysql-2v7f.lstack**),此时名字看着还是很不友好,我们先不用它。
|
||||
|
||||
### MySQL 配置进阶
|
||||
|
||||
上面完成了 MySQL 的基本安装配置。但是,实际使用中我们通常还有如下需求,需要我们对 MySQL 进行配置。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 开启外部访问
|
||||
|
||||
开启外部访问方便管理员操作 MySQL 数据库,也可以满足 K8s 集群之外的服务访问 MySQL 数据库的需求。
|
||||
|
||||
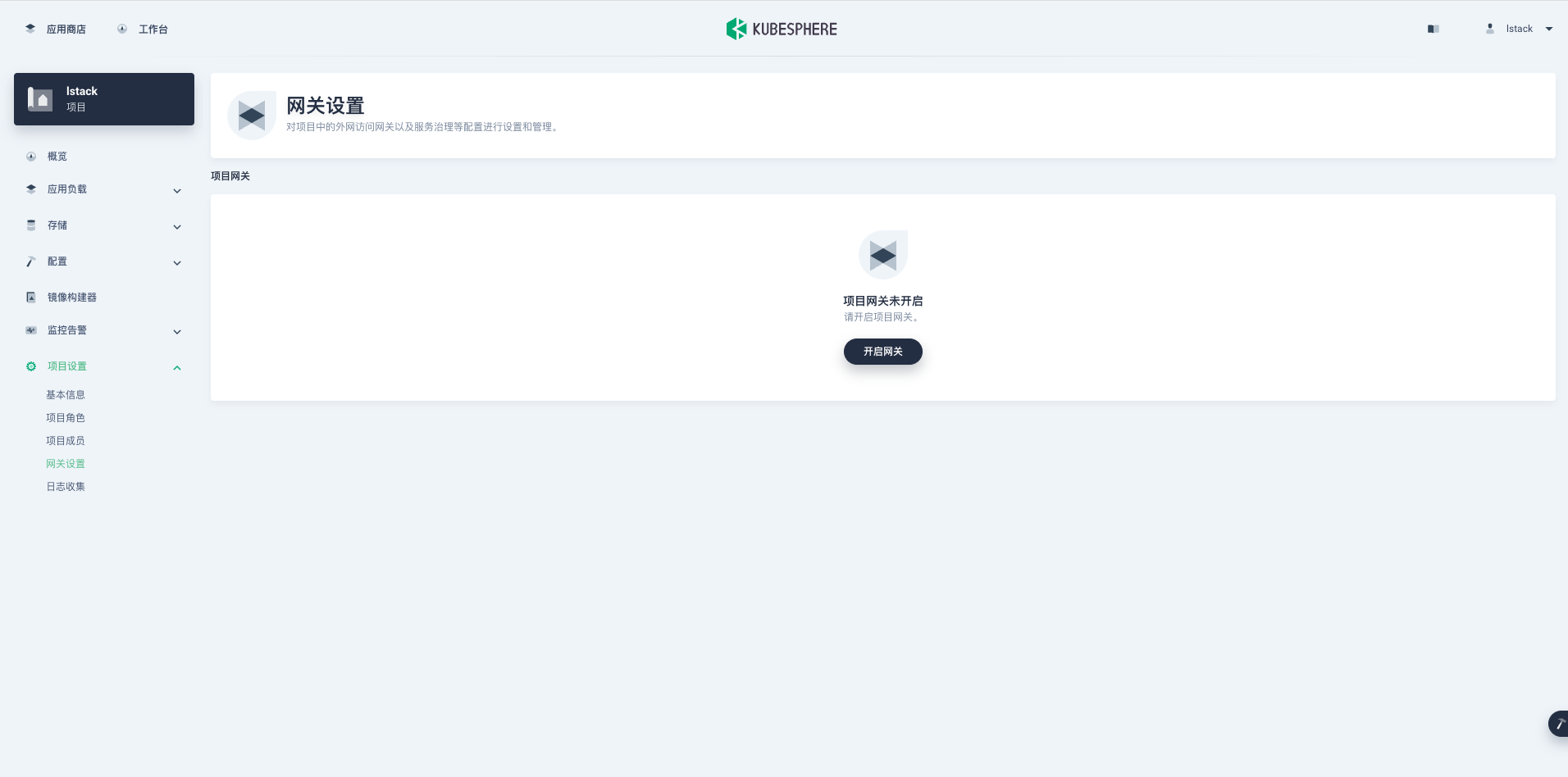
在 KubeSphere 中开启服务的外部访问需要先设置项目网关。
|
||||
|
||||
用项目管理员用户登录控制台。
|
||||
|
||||
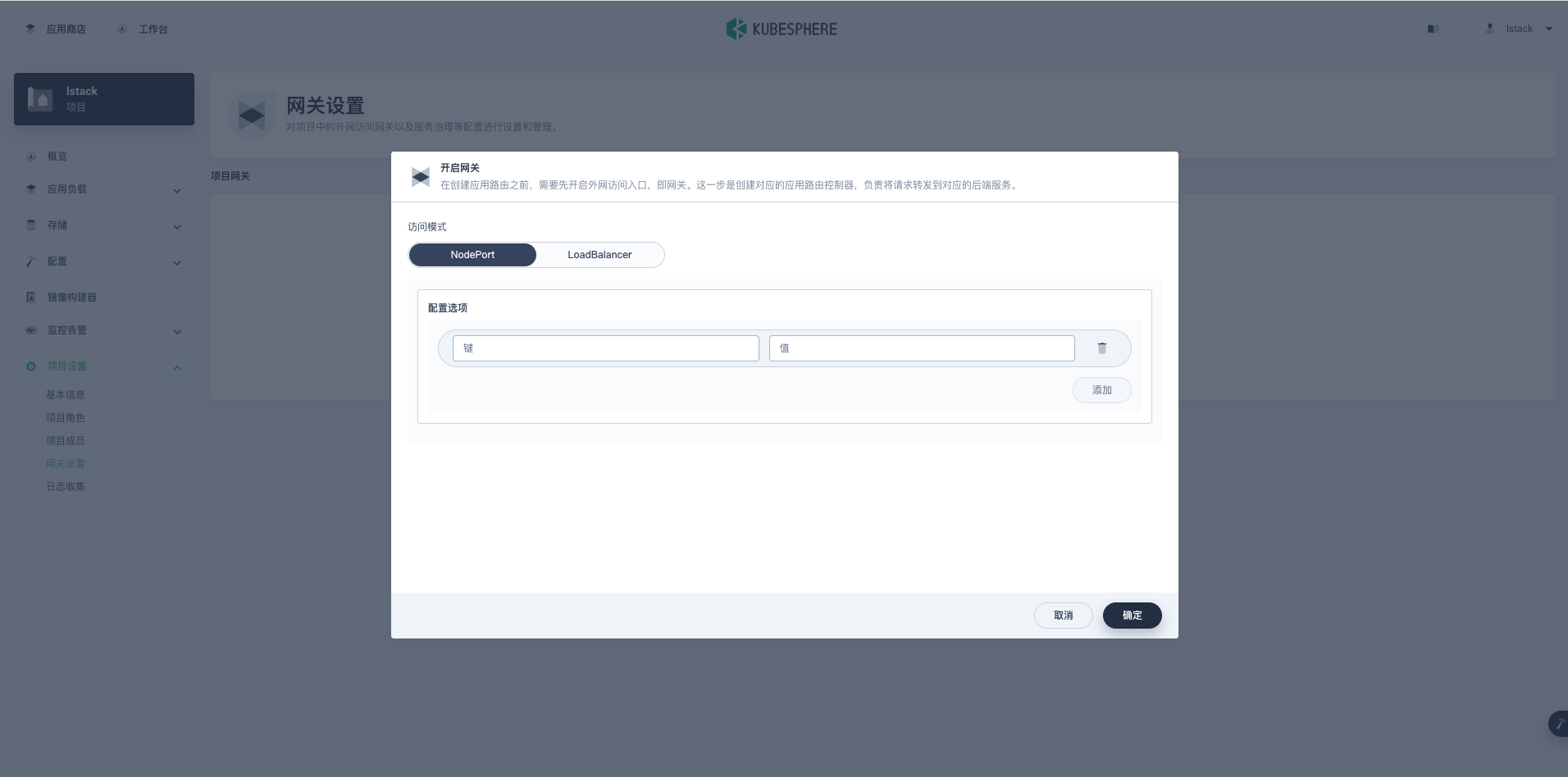
**工作台**->**项目**-> 点击**具体的项目**->**项目设置**->**网关设置**,点击**开启网关**。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
目前访问模式有 NodePort 和 LoadBalancer,但是 LoadBalancer 只支持公有云提供商云上的负载均衡器,所以我们只能选择 NodePort,点击确定。
|
||||
|
||||
**NodePort 模式里会创建一个采用了 nginx-ingress 的 kubesphere-router 的容器组,细节我们会在以后的专文探讨。**
|
||||
|
||||
<,>
|
||||
|
||||
网关设置的细节不在本文深入讨论,后续会有专文探讨。现在,做到这一步就 OK 了。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来创建一个 MySQL 服务用于对外提供服务。
|
||||
|
||||
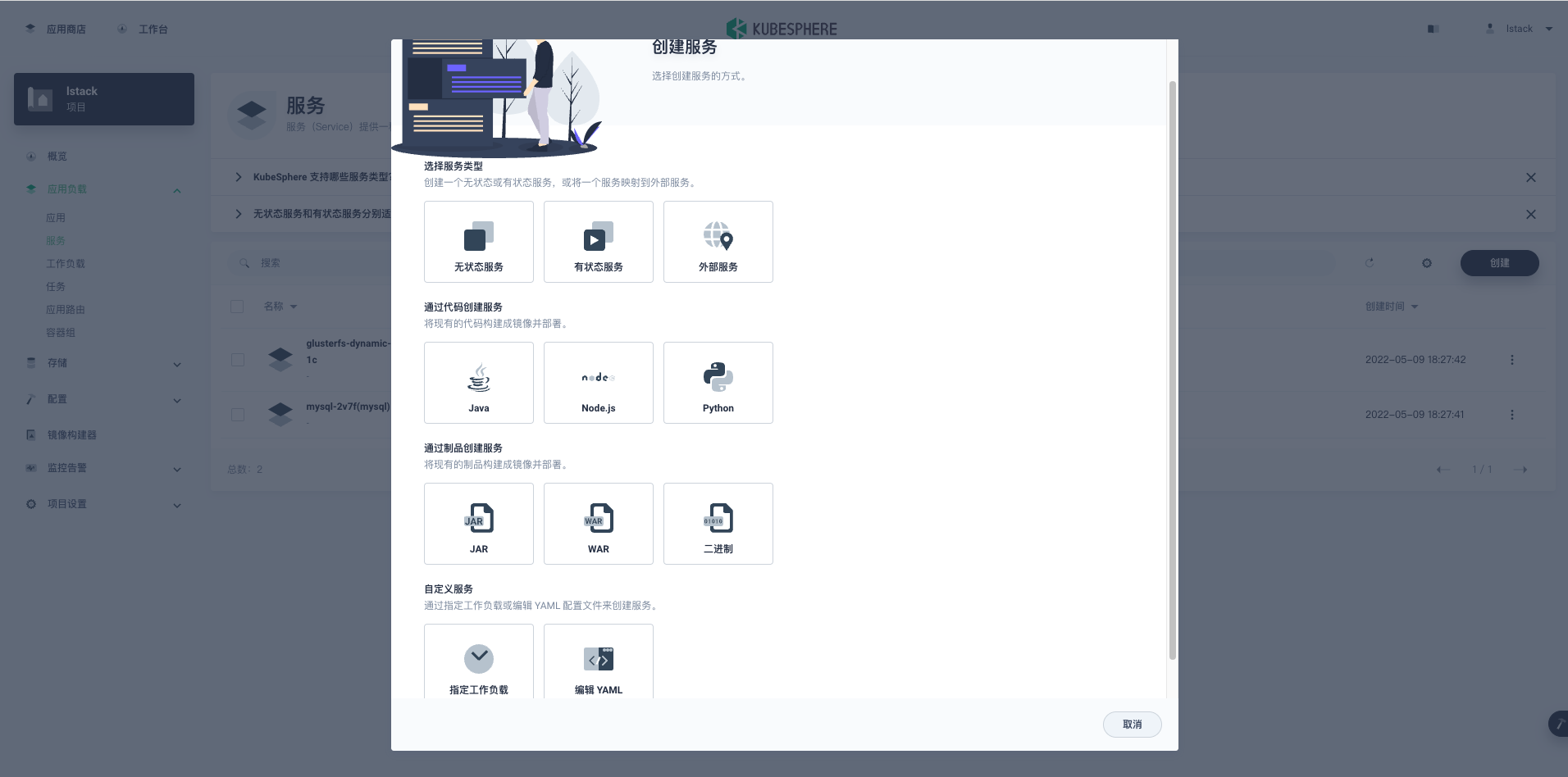
**应用负载**->-**服务**>**创建**-> 选择**自定义服务**->**指定工作负载**。
|
||||
|
||||
**这里有一个外部服务的选项,那个是基于 Ingress 使用域名访问的,不是目前我们想要的方式。**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
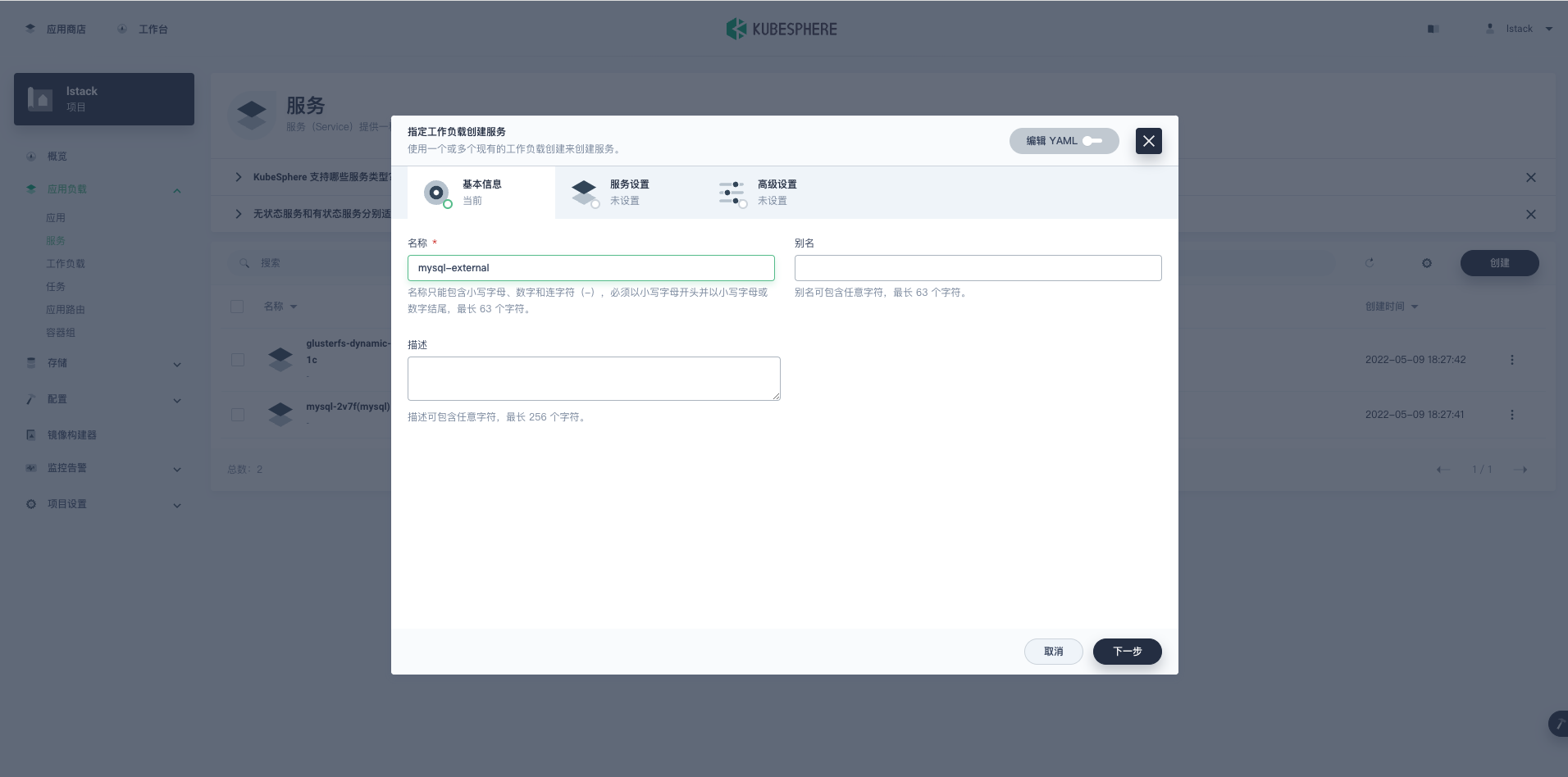
**指定工作负载创建服务-基本信息**。
|
||||
|
||||
- **名称:**mysql-external
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
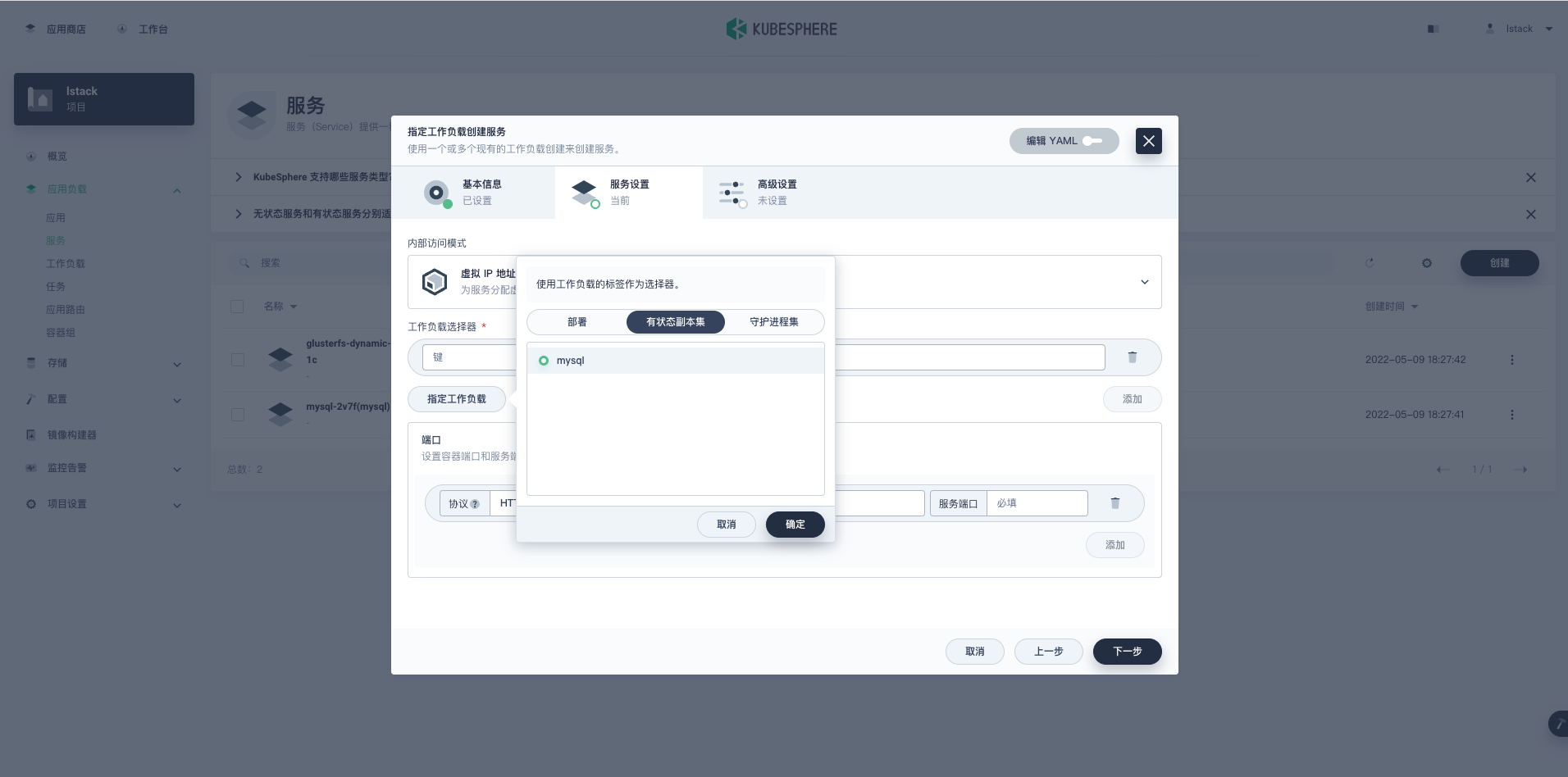
**指定工作负载创建服务-服务设置**,点击**指定工作负载**,选择**有状态副本集**->**mysql**,点击**确定**。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
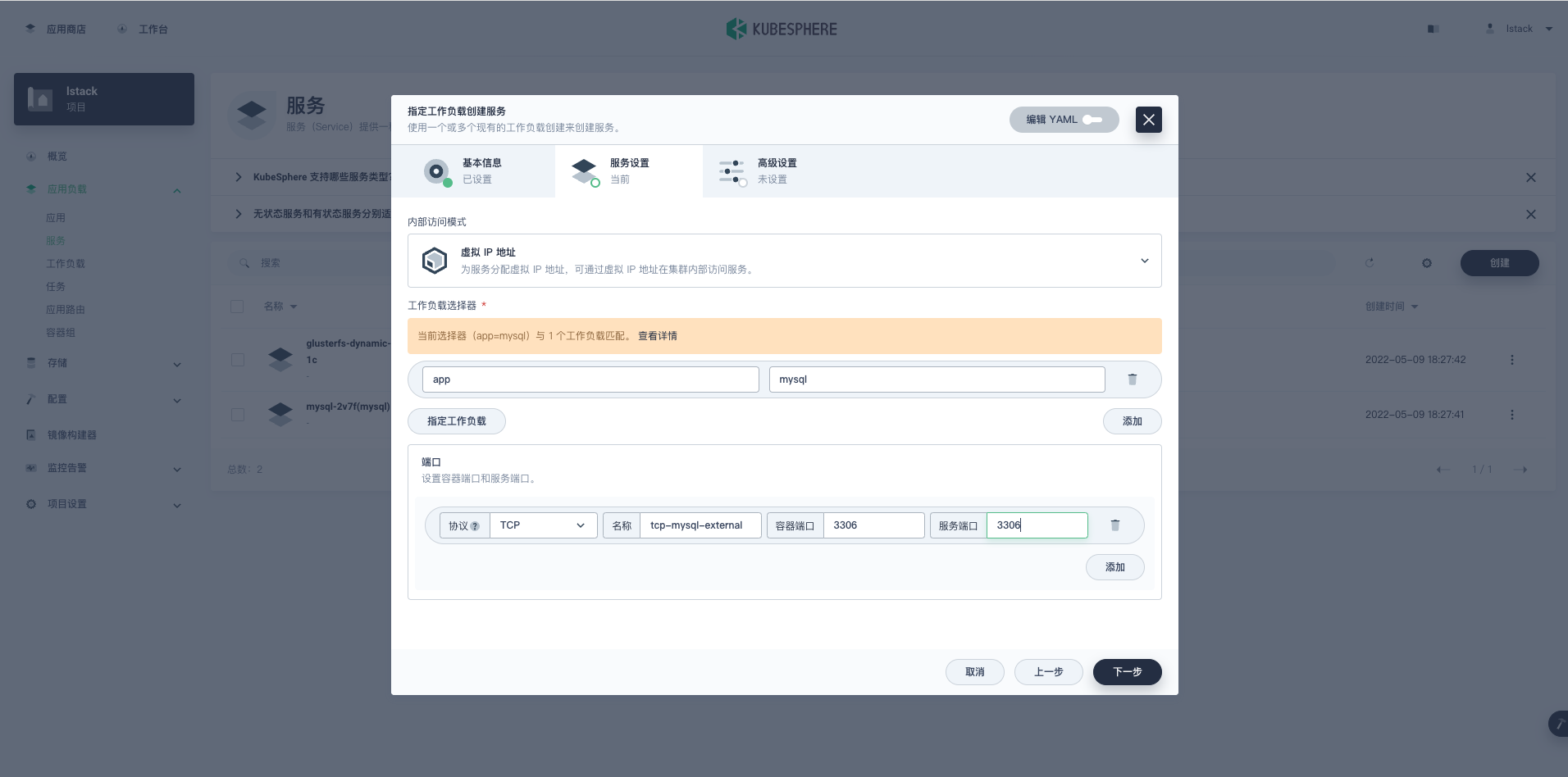
**指定工作负载创建服务-服务设置**,**端口**配置。
|
||||
|
||||
- **协议:** TCP
|
||||
- **名称:** tcp-mysql-external
|
||||
- **容器端口:** 3306
|
||||
- **服务端口:** 3306
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
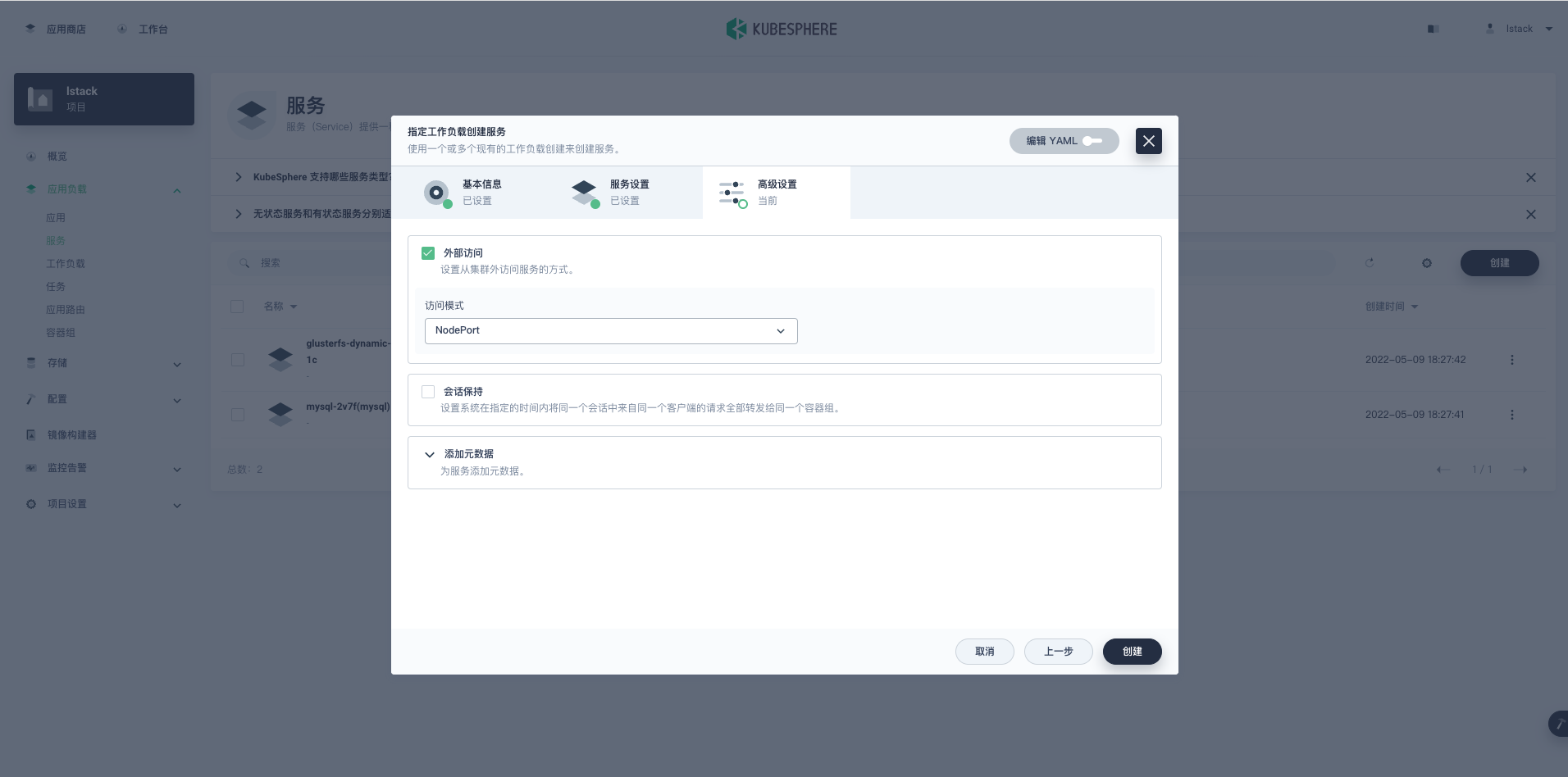
**指定工作负载创建服务-高级设置**。
|
||||
|
||||
- **外部访问:** **访问模式**选择 NodePort
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
完成所有设置后,点击**创建**,创建成功会自动返回服务列表,在服务列表中可以看到我们新创建的服务 **mysql-external** 及自动分配的外部访问端口号。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
先用 telnet 命令测试一下,MySQL 服务的连通性,能看到下面的结果就说明 MySQL 已经可以在 K8s 集群外部访问了。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
[root@ks-k8s-master-0 ~]# telnet 192.168.9.91 32529
|
||||
Trying 192.168.9.91...
|
||||
Connected to 192.168.9.91.
|
||||
Escape character is '^]'.
|
||||
EHost '10.233.117.0' is not allowed to connect to this MySQL serverConnection closed by foreign host.
|
||||
|
||||
# 细节!上面的EHost地址是192.168.9.91这个节点在K8s集群内部分配的IP
|
||||
[root@ks-k8s-master-0 ~]# ip add | grep 117 -B 2 -A 1
|
||||
7: tunl0@NONE: <NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1440 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
|
||||
link/ipip 0.0.0.0 brd 0.0.0.0
|
||||
inet 10.233.117.0/32 scope global tunl0
|
||||
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
|
||||
[root@ks-k8s-master-0 ~]# ip add | grep 91
|
||||
inet 192.168.9.91/24 brd 192.168.9.255 scope global noprefixroute ens160
|
||||
link/ether c6:d3:91:95:f1:0f brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 自定义 MySQL 配置文件
|
||||
|
||||
默认安装的 MySQL 使用的 my.cnf 配置文件,适配的使用场景有限,所以自定义 mysql 配置文件是必然要做的一项配置。
|
||||
|
||||
这里我随机找了一份配置文件,仅仅是为了实现自定义配置的功能,请根据自己的使用场景使用合适的自定义配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
使用自定义配置前,我们先需要了解目前 mysql 容器的配置文件结构。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 KubeSphere 提供的**终端**工具,进入 mysql 容器内部,执行下面的命令,分析执行结果 (终端登录方式参考前文截图)。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# bash
|
||||
root@mysql-0:/# ls /etc/mysql/ -l
|
||||
total 8
|
||||
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 62 Apr 28 06:20 conf.d
|
||||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 24 Apr 28 06:20 my.cnf -> /etc/alternatives/my.cnf
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 839 Aug 3 2016 my.cnf.fallback
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1200 Mar 22 01:44 mysql.cnf
|
||||
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 24 Apr 28 06:20 mysql.conf.d
|
||||
|
||||
root@mysql-0:/# ls /etc/mysql/conf.d/ -l
|
||||
total 12
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 43 Apr 28 06:20 docker.cnf
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 8 Aug 3 2016 mysql.cnf
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 55 Aug 3 2016 mysqldump.cnf
|
||||
|
||||
root@mysql-0:/# ls /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/ -l
|
||||
total 4
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1589 Apr 28 06:20 mysqld.cnf
|
||||
|
||||
root@mysql-0:/# ls -l /etc/alternatives/my.cnf
|
||||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 20 Apr 28 06:20 /etc/alternatives/my.cnf -> /etc/mysql/mysql.cnf
|
||||
|
||||
root@mysql-0:/# cat /etc/mysql/mysql.cnf
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2016, 2021, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
|
||||
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License, version 2.0,
|
||||
# as published by the Free Software Foundation.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# This program is also distributed with certain software (including
|
||||
# but not limited to OpenSSL) that is licensed under separate terms,
|
||||
# as designated in a particular file or component or in included license
|
||||
# documentation. The authors of MySQL hereby grant you an additional
|
||||
# permission to link the program and your derivative works with the
|
||||
# separately licensed software that they have included with MySQL.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
|
||||
# GNU General Public License, version 2.0, for more details.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
|
||||
# along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||
# Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
|
||||
|
||||
!includedir /etc/mysql/conf.d/
|
||||
!includedir /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/
|
||||
|
||||
## 挑两个配置文件看看
|
||||
root@mysql-0:~# cat /etc/mysql/conf.d/docker.cnf
|
||||
[mysqld]
|
||||
skip-host-cache
|
||||
skip-name-resolve
|
||||
|
||||
root@mysql-0:~# cat /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2014, 2021, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
|
||||
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License, version 2.0,
|
||||
# as published by the Free Software Foundation.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# This program is also distributed with certain software (including
|
||||
# but not limited to OpenSSL) that is licensed under separate terms,
|
||||
# as designated in a particular file or component or in included license
|
||||
# documentation. The authors of MySQL hereby grant you an additional
|
||||
# permission to link the program and your derivative works with the
|
||||
# separately licensed software that they have included with MySQL.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
|
||||
# GNU General Public License, version 2.0, for more details.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
|
||||
# along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||
# Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
|
||||
|
||||
#
|
||||
# The MySQL Server configuration file.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# For explanations see
|
||||
# http://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysql/en/server-system-variables.html
|
||||
|
||||
[mysqld]
|
||||
pid-file = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
|
||||
socket = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock
|
||||
datadir = /var/lib/mysql
|
||||
#log-error = /var/log/mysql/error.log
|
||||
# By default we only accept connections from localhost
|
||||
#bind-address = 127.0.0.1
|
||||
# Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted security risks
|
||||
symbolic-links=0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
分析上面的输出我们得到以下结论。
|
||||
|
||||
- 根配置文件:**/etc/mysql/mysql.cnf**
|
||||
|
||||
- 自定义的配置文件可以存放在 **/etc/mysql/conf.d/** 或 **/etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/** 目录下
|
||||
|
||||
- 通过上面的结论,发现有两种方式实现自定义配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
- 直接替换 **/etc/mysql/mysql.cnf**
|
||||
|
||||
> **适用于个性化配置较多较复杂的场景,比如 50+的配置项。**
|
||||
|
||||
- 将自定义的配置放在 **/etc/mysql/conf.d/** 或 **/etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/** 目录下,根据官方配置使用情况,建议选择 **/etc/mysql/conf.d/**
|
||||
|
||||
> **适用于自定义配置较少的场景,比如只是为了开启个别功能,或是个别默认参数不符合使用需求**
|
||||
|
||||
本文采用第二种方式,采用一个独立的 custom.cnf 文件配置以下参数。
|
||||
|
||||
```ini
|
||||
[mysqld]
|
||||
#performance setttings
|
||||
lock_wait_timeout = 3600
|
||||
open_files_limit = 65535
|
||||
back_log = 1024
|
||||
max_connections = 512
|
||||
max_connect_errors = 1000000
|
||||
table_open_cache = 1024
|
||||
table_definition_cache = 1024
|
||||
thread_stack = 512K
|
||||
sort_buffer_size = 4M
|
||||
join_buffer_size = 4M
|
||||
read_buffer_size = 8M
|
||||
read_rnd_buffer_size = 4M
|
||||
bulk_insert_buffer_size = 64M
|
||||
thread_cache_size = 768
|
||||
interactive_timeout = 600
|
||||
wait_timeout = 600
|
||||
tmp_table_size = 32M
|
||||
max_heap_table_size = 32M
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
实现思路。
|
||||
|
||||
- K8s 中我们可以通过配置 ConfigMap 的方式将文件挂载给容器
|
||||
- 将自定义的 MySQL 配置文件,定义为一个 ConfigMap
|
||||
- 将 ConfigMap 挂载给 MySQL 的容器
|
||||
|
||||
创建 ConfigMap 配置文件,**配置**->**配置字典**,点击**创建**。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
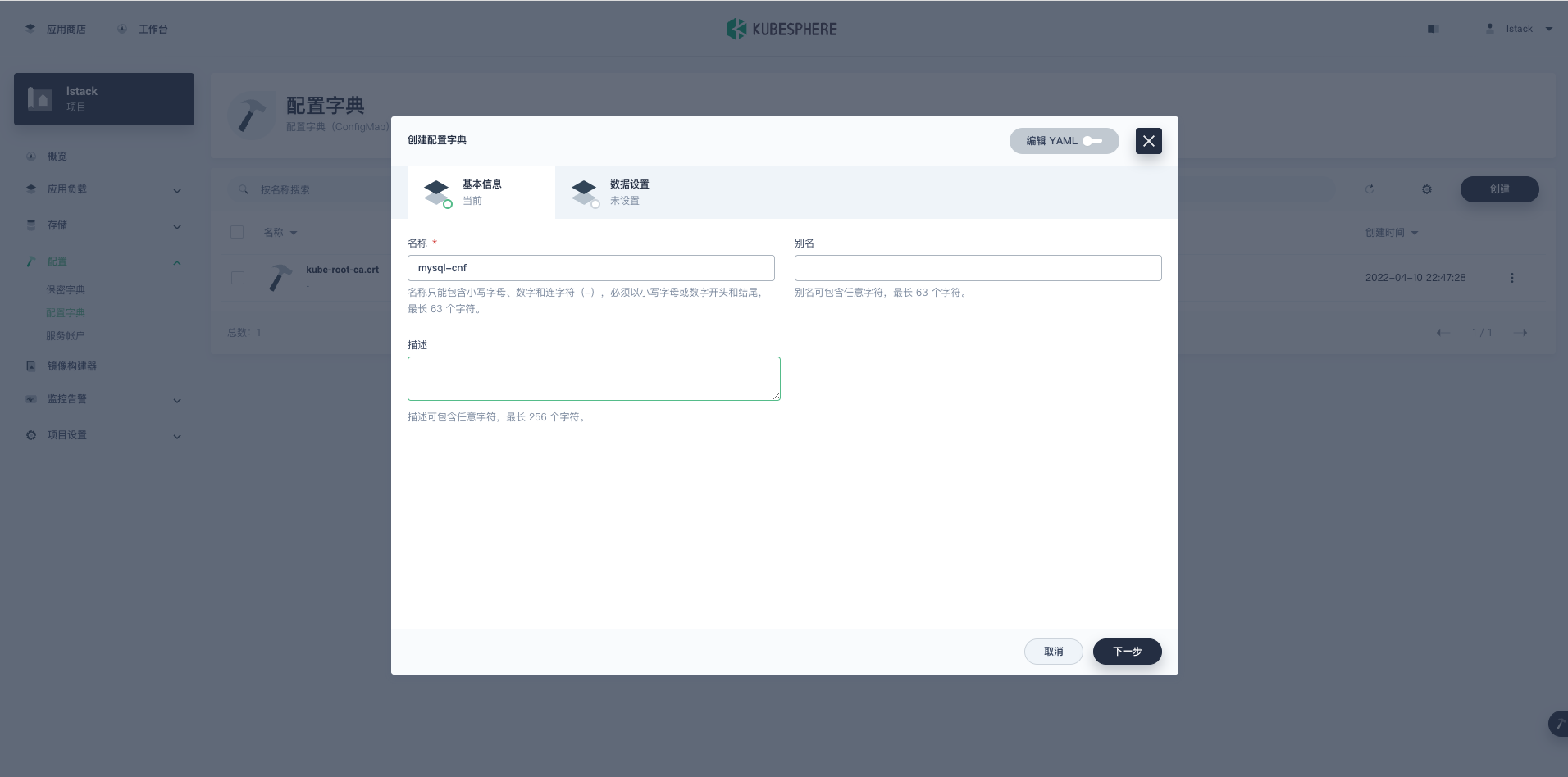
**创建配置字典-基本信息**。
|
||||
|
||||
- 名称:mysql-cnf
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**创建配置字典-数据设置**。
|
||||
|
||||
- 点击**添加数据**
|
||||
- **键:** custom.cnf
|
||||
- **值:** 粘贴上面的配置参数
|
||||
|
||||
<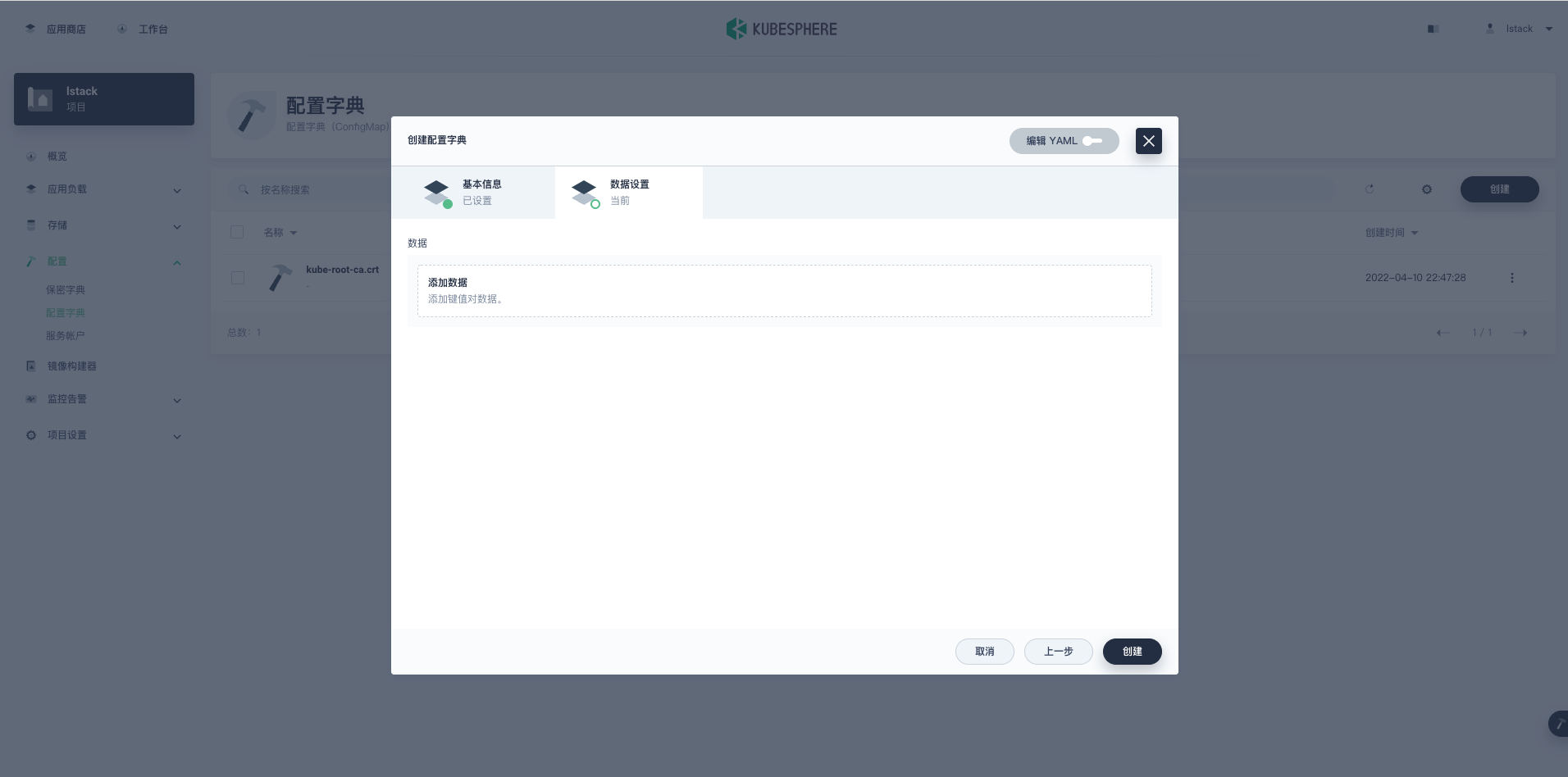,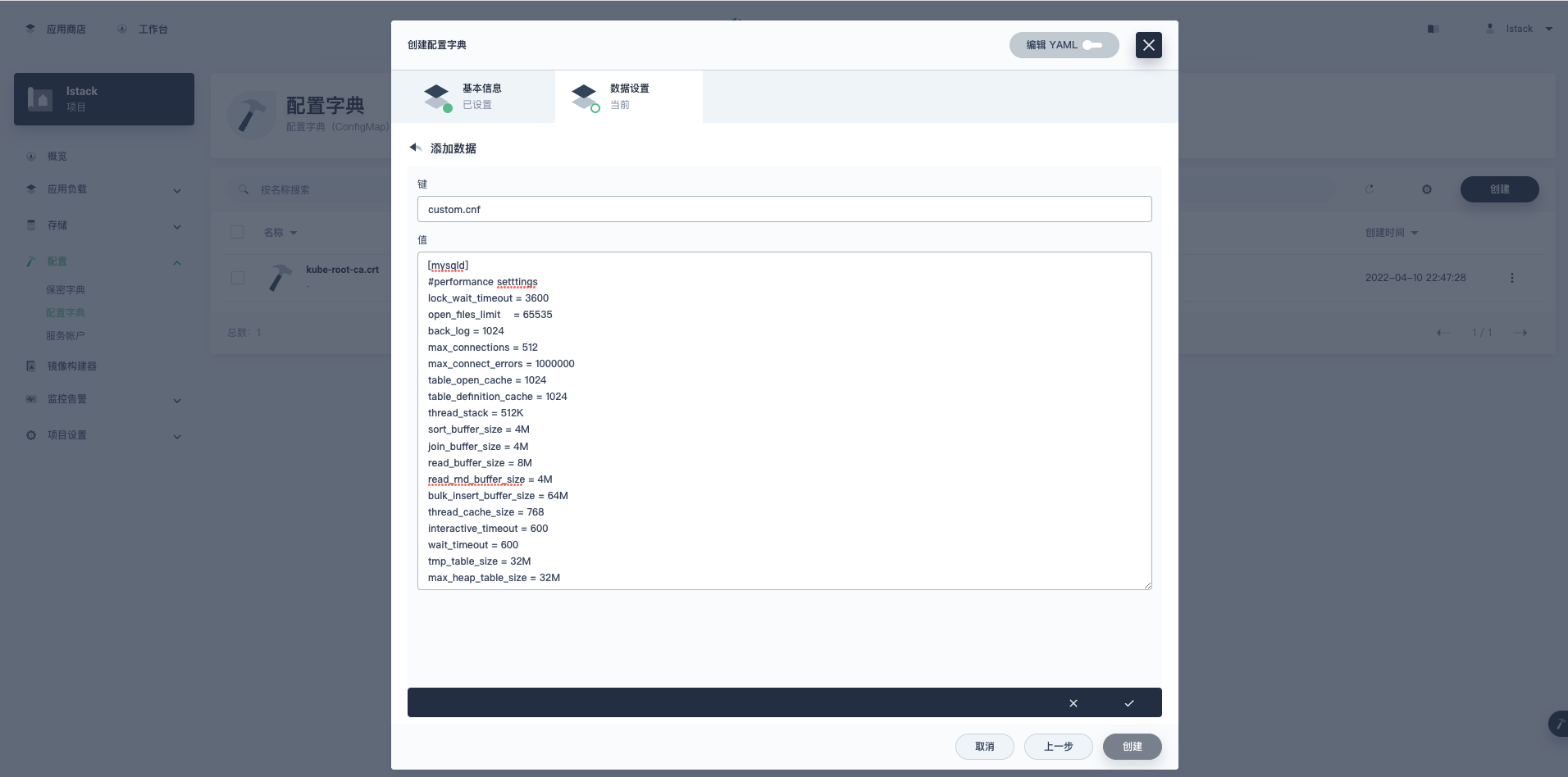>
|
||||
|
||||
填写完键值信息后,点击**对号**确定,最后点击**创建**,创建完成后会返回**配置字典**页面。
|
||||
|
||||
<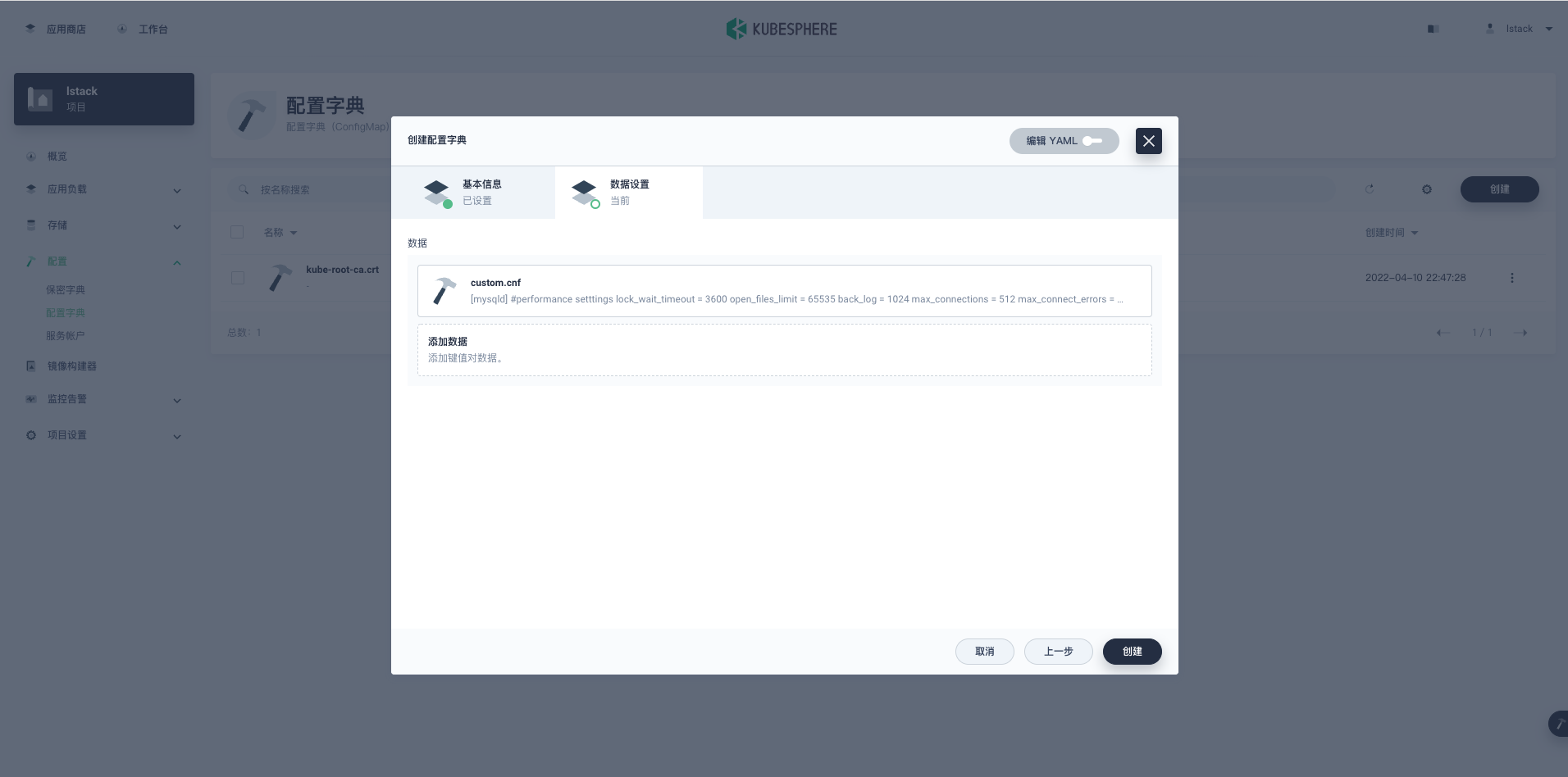,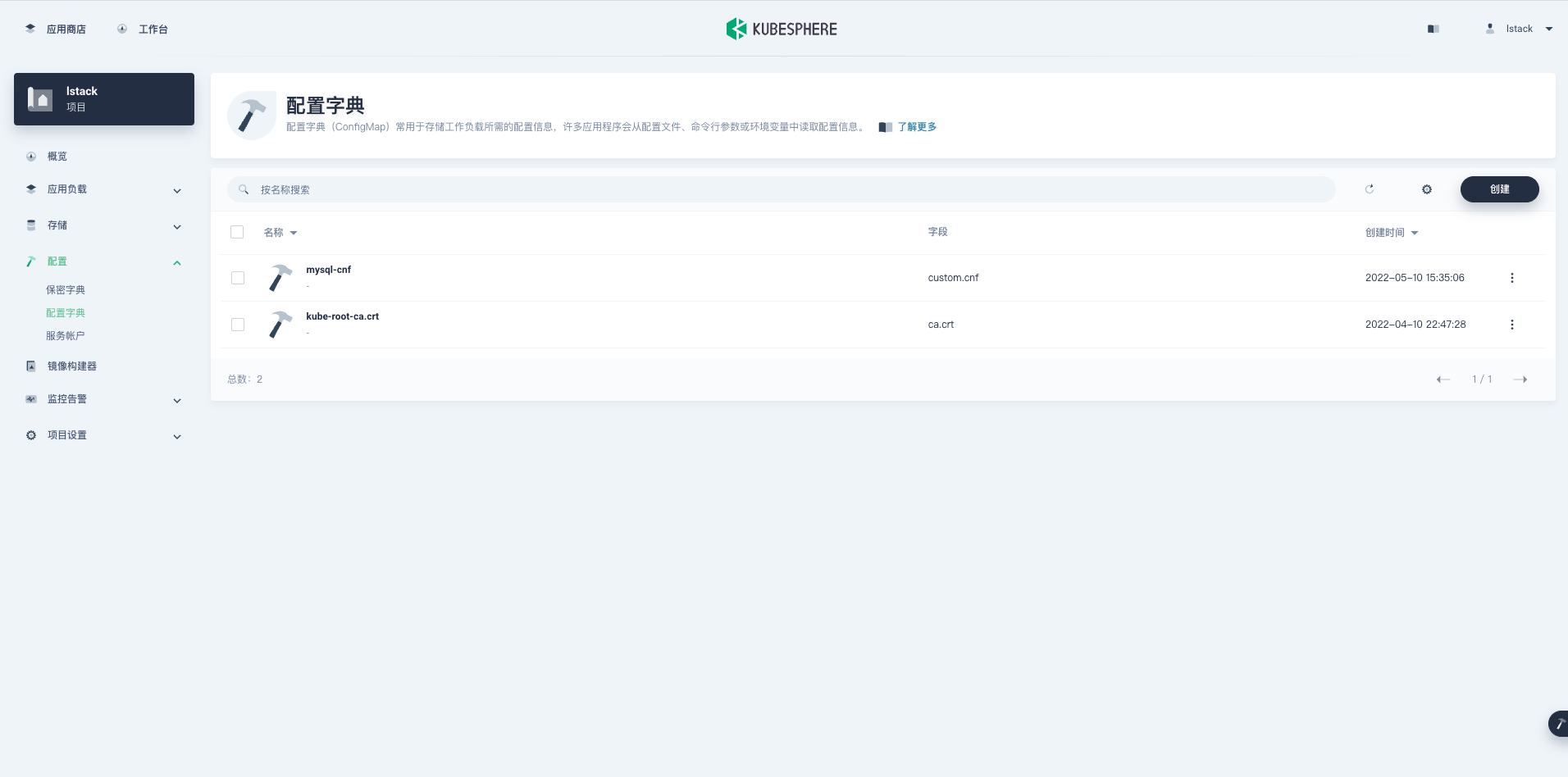>
|
||||
|
||||
接下来将自定义配置文件,挂载到 MySQL 容器。
|
||||
|
||||
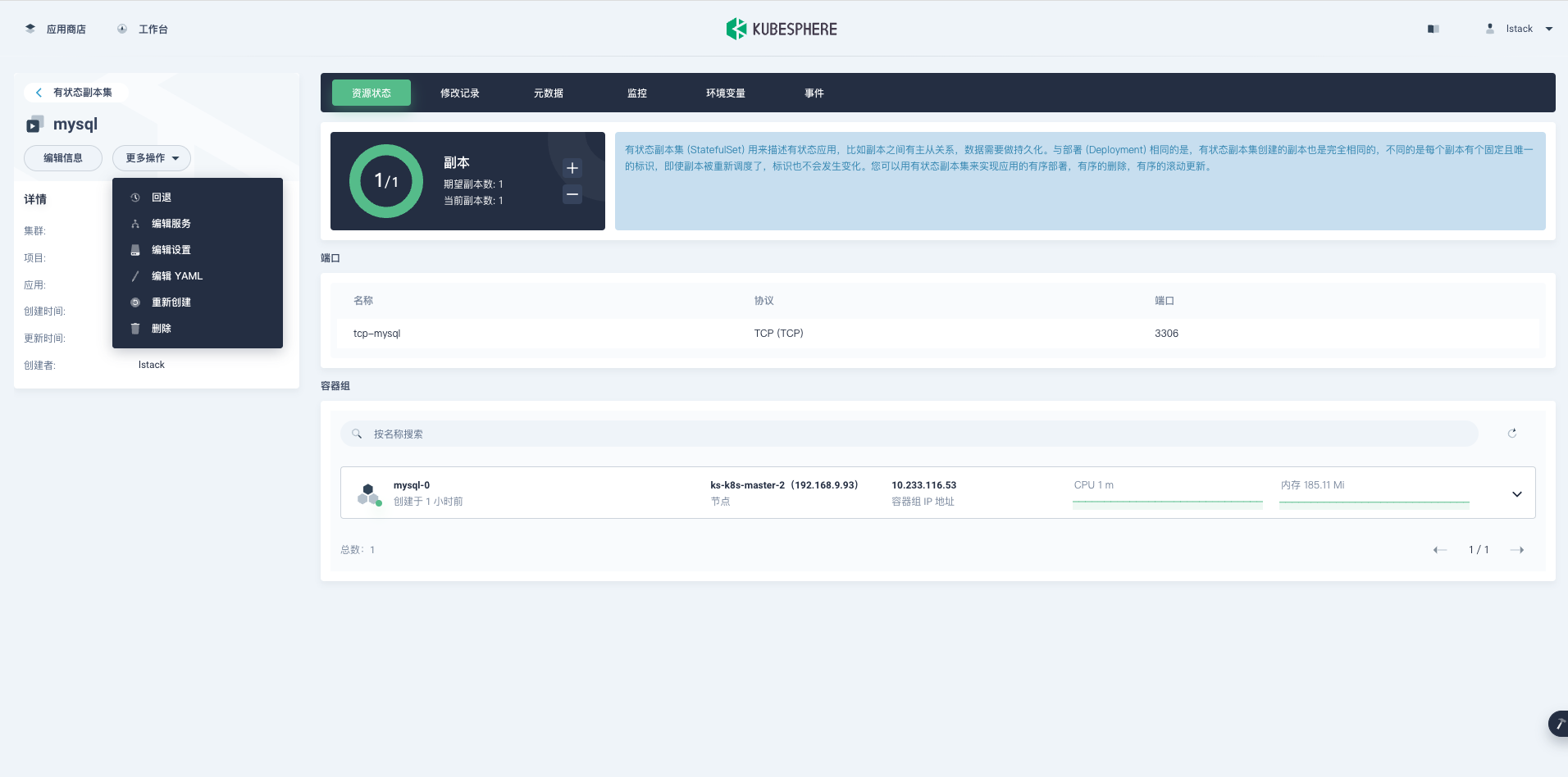
**应用负载**->**工作负载**->**有状态副本集**-> 点击 **mysql**-> 进入详细配置页面->**更多操作**-点击**编辑设置**。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
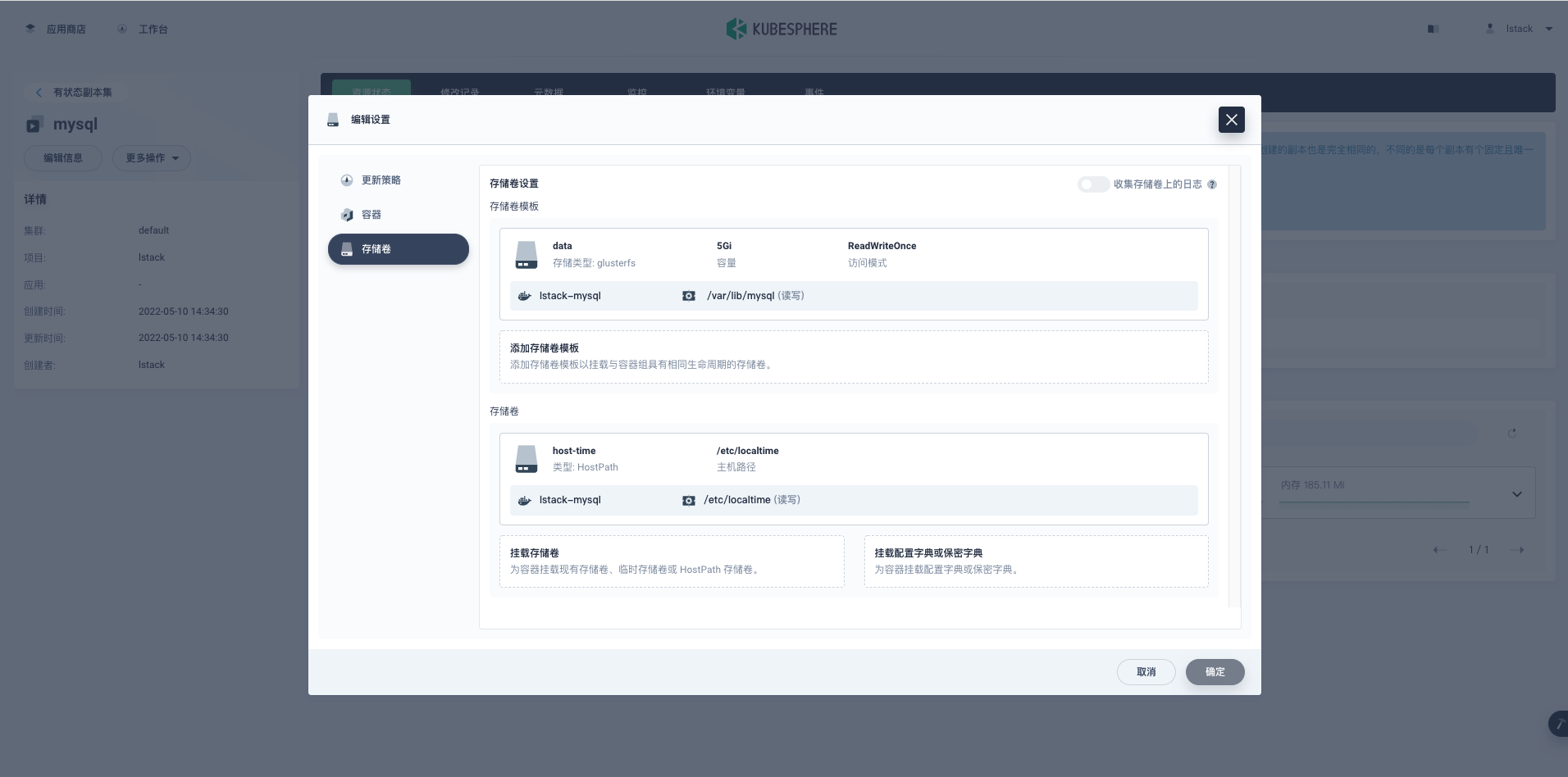
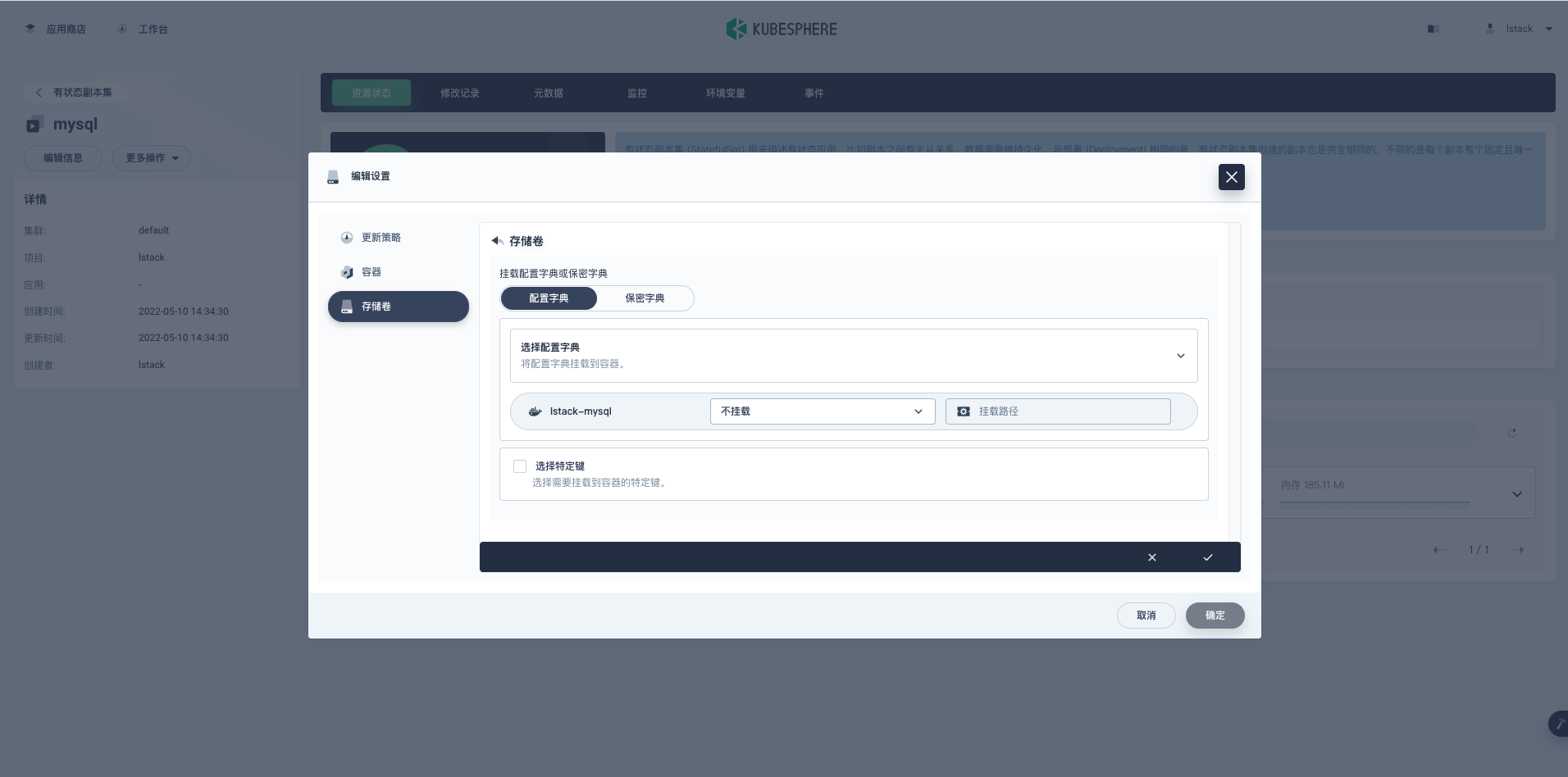
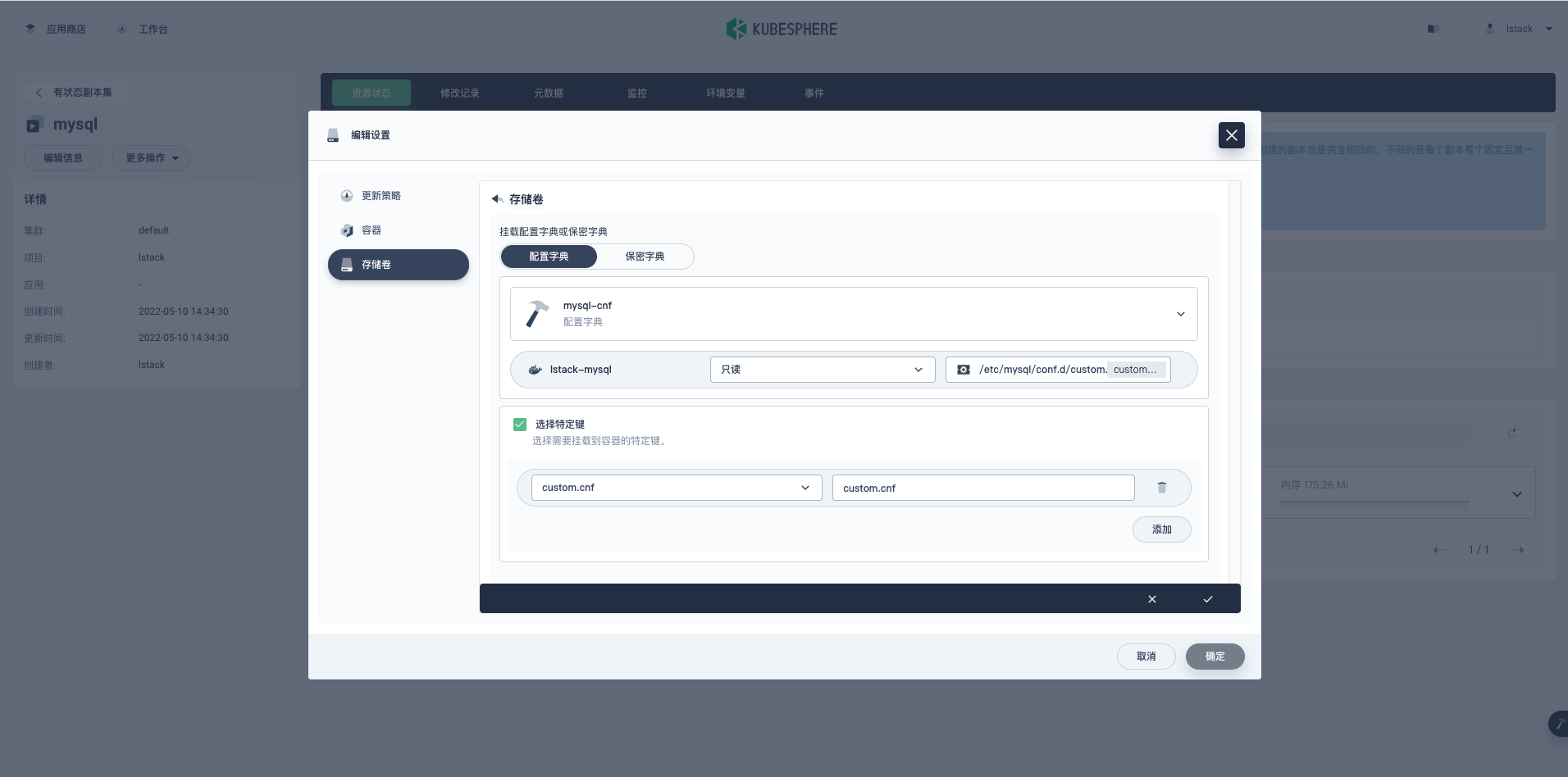
**编辑设置**->**存储卷**->**挂载配置字典或保密字典**。
|
||||
|
||||
<,>
|
||||
|
||||
**存储卷**。
|
||||
|
||||
- **选择配置字典:**mysql-cnf
|
||||
- **只读**
|
||||
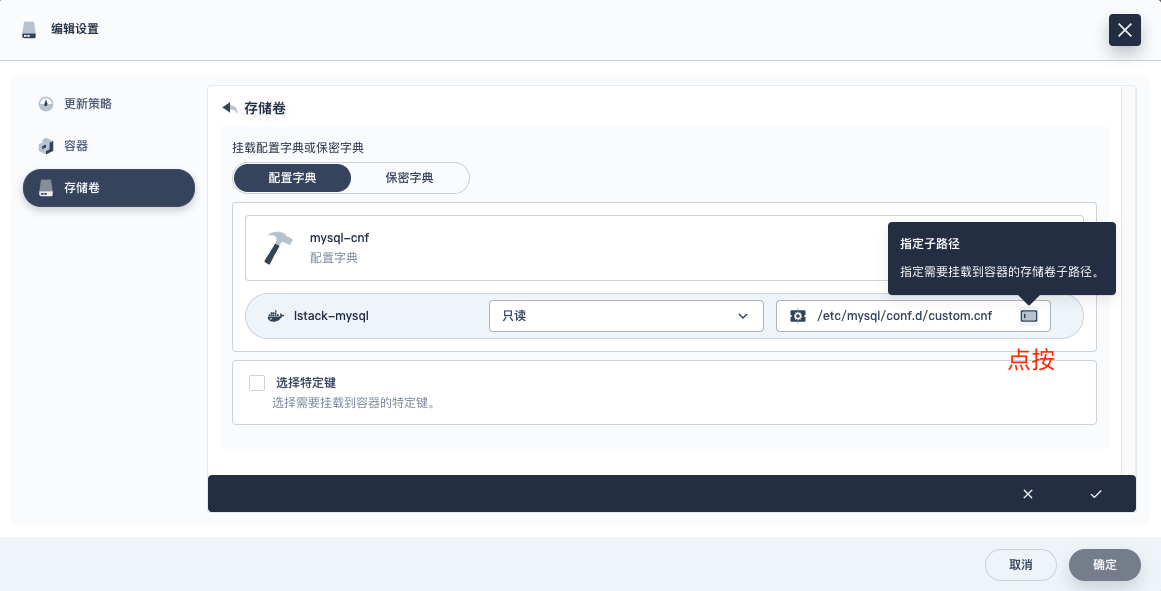
- **挂载路径:**/etc/mysql/conf.d/custom.cnf
|
||||
- 指定子路径:custom.cnf
|
||||
- **此处必须这么写,否则会覆盖掉指定目录下的所有已存在文件**
|
||||
- **底层就是 subPath**
|
||||
- **具体操作看下图图示,注意细节**
|
||||
- **选择特定键:**
|
||||
- 键:custom.cnf
|
||||
- 路径:custom.cnf
|
||||
|
||||
<,,>
|
||||
|
||||
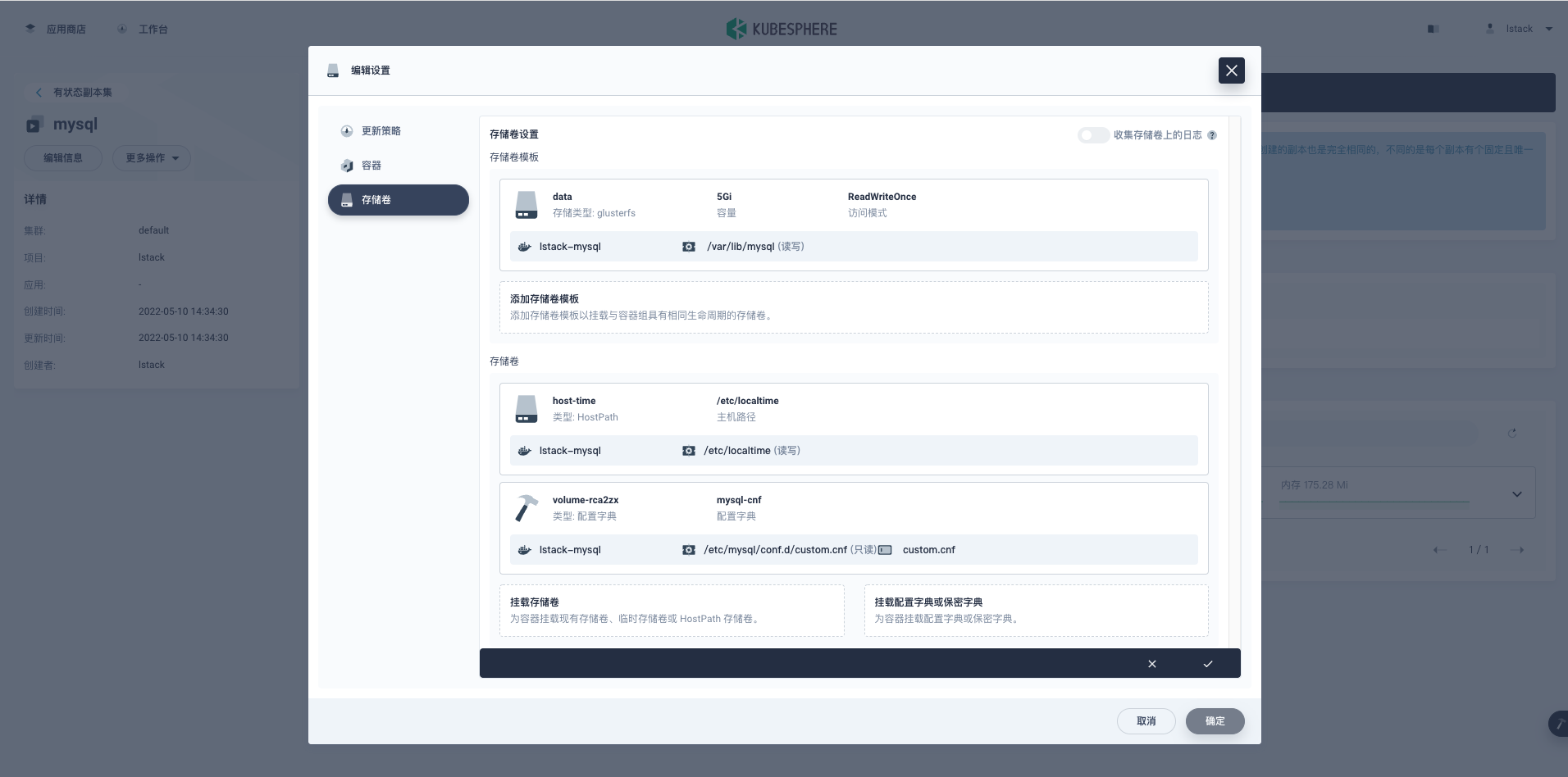
输入完成后,点击**对号**。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
再次点击**对号**,点击**确定**,mysql 容器会自动开始重建。
|
||||
|
||||
<,>
|
||||
|
||||
重建成功后我们验证一下配置文件是否成功挂载。
|
||||
|
||||
先看一下容器组的配置,发现新增了一个存储卷 **volume-xxxx**。
|
||||
|
||||
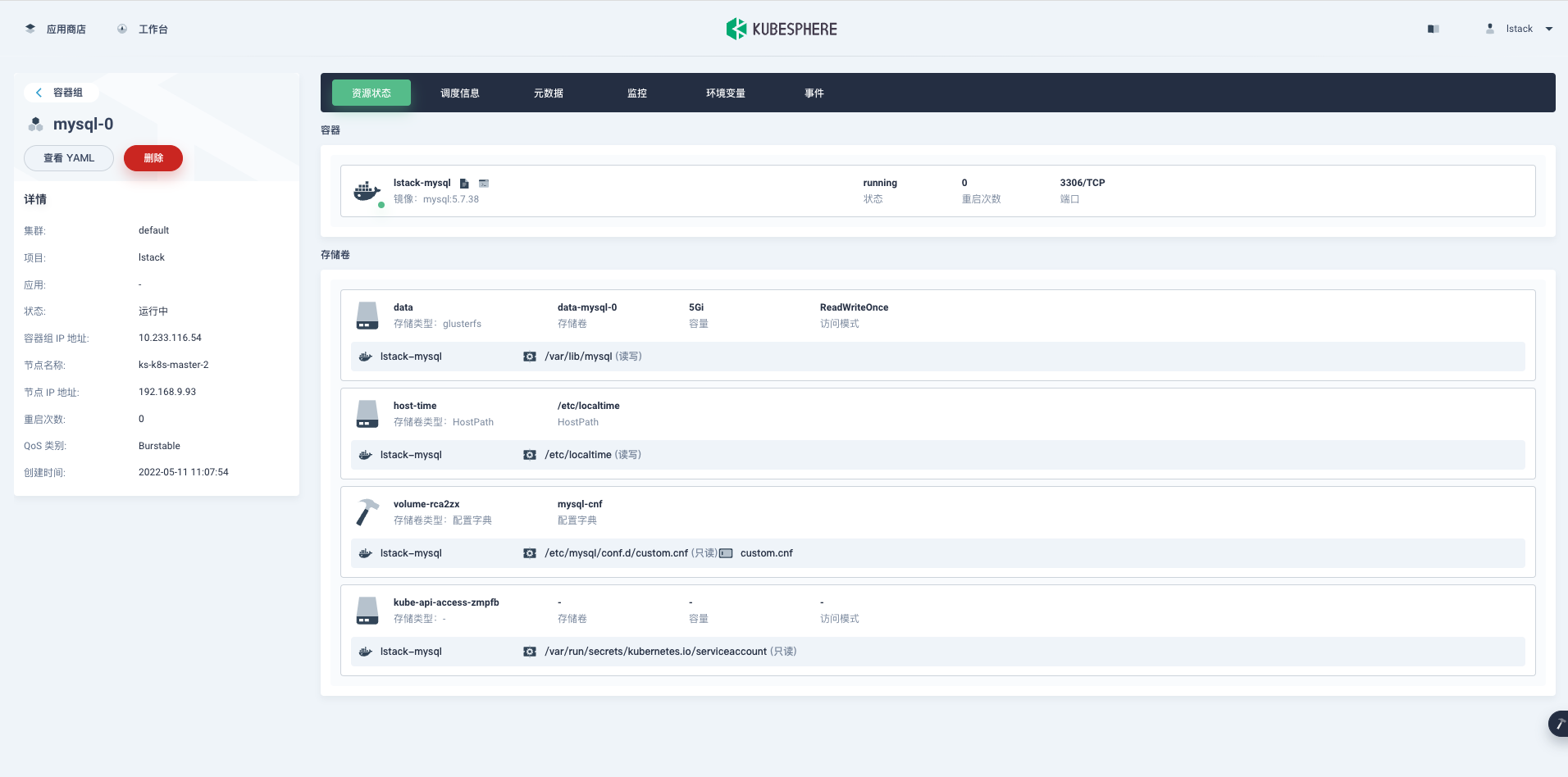
|
||||
|
||||
**终端**-> 进入容器内部查看。
|
||||
|
||||
查看配置文件挂载和文件内容。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# bash
|
||||
root@mysql-0:/# ls /etc/mysql/conf.d/
|
||||
custom.cnf docker.cnf mysql.cnf mysqldump.cnf
|
||||
|
||||
root@mysql-0:/# ls -l /etc/mysql/conf.d/
|
||||
total 16
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 463 May 11 11:07 custom.cnf
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 43 Apr 28 06:20 docker.cnf
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 8 Aug 3 2016 mysql.cnf
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 55 Aug 3 2016 mysqldump.cnf
|
||||
|
||||
root@mysql-0:/# cat /etc/mysql/conf.d/custom.cnf
|
||||
[mysqld]
|
||||
#performance setttings
|
||||
lock_wait_timeout = 3600
|
||||
open_files_limit = 65535
|
||||
back_log = 1024
|
||||
max_connections = 512
|
||||
max_connect_errors = 1000000
|
||||
table_open_cache = 1024
|
||||
table_definition_cache = 1024
|
||||
thread_stack = 512K
|
||||
sort_buffer_size = 4M
|
||||
join_buffer_size = 4M
|
||||
read_buffer_size = 8M
|
||||
read_rnd_buffer_size = 4M
|
||||
bulk_insert_buffer_size = 64M
|
||||
thread_cache_size = 768
|
||||
interactive_timeout = 600
|
||||
wait_timeout = 600
|
||||
tmp_table_size = 32M
|
||||
max_heap_table_size = 32M
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
查看配置参数是否生效。
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
root@mysql-0:/# mysql -u root -p
|
||||
Enter password:
|
||||
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
|
||||
Your MySQL connection id is 2
|
||||
Server version: 5.7.38 MySQL Community Server (GPL)
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2000, 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
|
||||
|
||||
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
|
||||
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
|
||||
owners.
|
||||
|
||||
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'max_connect%';
|
||||
+--------------------+---------+
|
||||
| Variable_name | Value |
|
||||
+--------------------+---------+
|
||||
| max_connect_errors | 1000000 |
|
||||
| max_connections | 512 |
|
||||
+--------------------+---------+
|
||||
2 rows in set (0.02 sec)
|
||||
|
||||
mysql>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
执行结果跟我们的配置一致,说明配置成功。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 导入数据库数据
|
||||
|
||||
将数据库文件(SQL),挂载到容器的指定目录下 **/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d**,容器创建时会自动导入(**非必要不推荐**)。
|
||||
|
||||
用数据库管理工具远程管理数据库(**推荐**)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 总结
|
||||
|
||||
本文详细介绍了 KubeSphere 图形化部署单节点 MySQL 上的安装配置过程,如何利用 KubeSphere 的图形化功能创建资源配置清单 YAML 文件的思路和具体操作过程,以后再部署其他在官网找不到详细配置指南的服务都可以借鉴这个方法。
|
||||
|
||||
下篇文章将会介绍 GitOps 的基本概念并演示如何用 GitOps 理念在原生 K8s 上部署 MySQL 服务。
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue